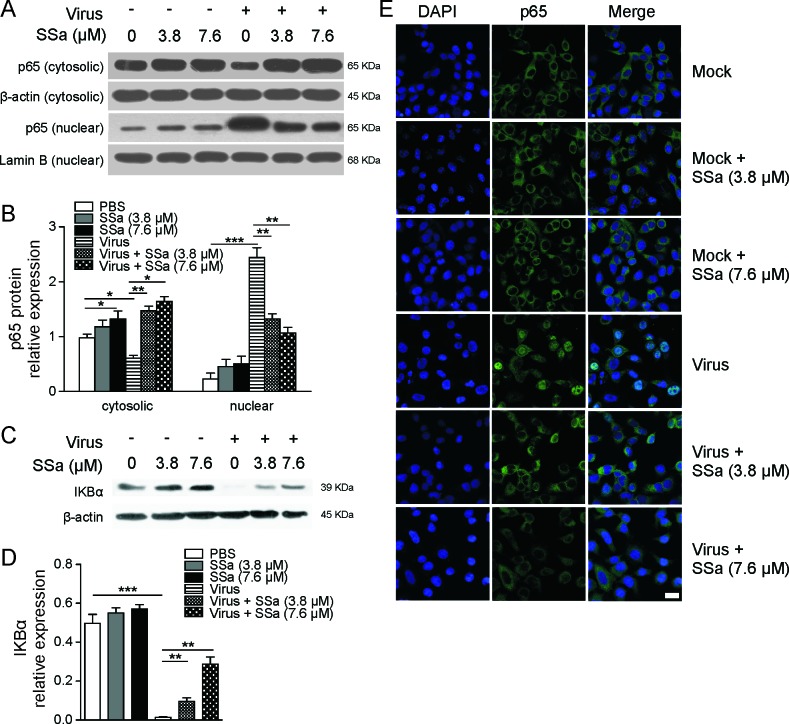
Figure 2. SSa inhibits nuclear NF-κB protein translocation in H5N1 infected A549 cells.
A. and B. A549 cells infected with H5N1 IAV (MOI = 0.1, 1 h) and cultured ± 3.8 or 7.6 μM SSa were harvested 24 h post-infection. Non-infected A549 cells were also cultured ± 3.8 or 7.6 μM SSa and harvested at the same time point. A. Cytosolic and nuclear immunoblotting was conducted for NF-κB p65 subunit expression with lamin B1 (nuclear) and β-actin (cytosolic) loading controls. Results are representative of three independent immunoblotting experiments. B. Relative gray scale values of cytosolic and nuclear p65 expression from three independent immunoblotting assays as depicted in A.. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. C. Immunoblotting of A549 cells lysed at 24 h post-infection for total protein IκBα expression with β-actin as a loading control. Non-infected A549 cells were also cultured ± 3.8 or 7.6 μM SSa and harvested at the same time point. Results are representative of three independent immunoblotting experiments. D. Relative gray scale values of total protein IκBα expression quantified from C. *P < 0.05. E. H5N1-infected A549 cells (MOI = 1, 1 h) were cultured ± 3.8 or 7.6 μM SSa for 8 h post-infection, fixed and stained for p65 expression (p65: green, DAPI nuclear stain: blue, scale = 10 μm). Representative of three independent experiments. Non-infected ± 3.8 or 7.6 μM SSa treated A549 cells were visualised in parallel.