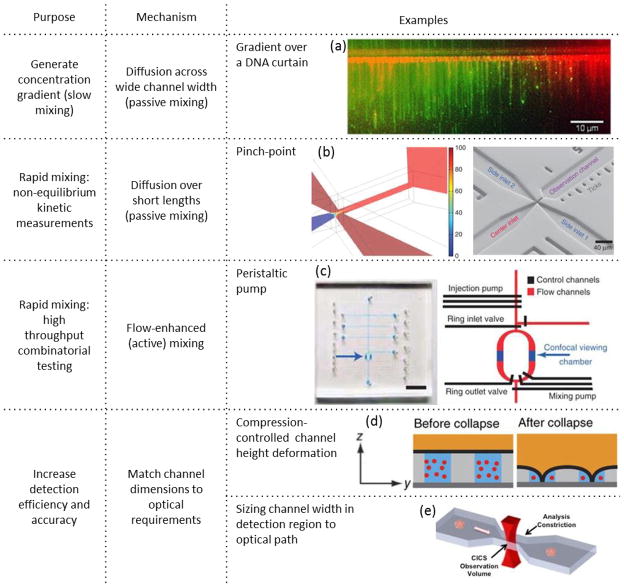
Figure 8.
Microfluidic tools and operations are used to enhance observation and analysis of interactions involving single nucleic acid molecules. Stable concentration gradients, generated by diffusion across flow streams in a microchannel, enable analysis of protein/DNA interactions on a DNA curtain over a continuous range of protein concentrations in a single experiment (picture reprinted from ref. 198 copyright 2013, with permission from Elsevier). Rapid mixing at a channel constriction coupled with convective flow can be used to observe fast kinetics through spatial separation (figure reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Protocols ref. 203, copyright 2013). Rapid pump mixing can also be used for high throughput combinatorial screening separation (figure reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Methods ref.204, copyright 2011). Microchannel constrictions can also be used to enhance detection efficiency by matching the microfluidic chamber dimensions to the optical detection volume. This has been demonstrated in both z-dimension with compression of channel height (figure reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Nature Methods ref. 205, copyright 2014), and x-dimension through microfabricated cross-section constriction (figure reproduced from ref. 206).