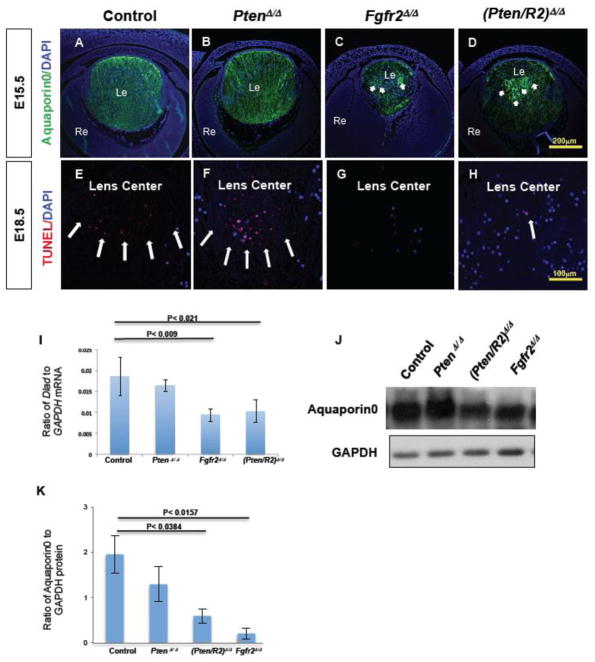
Figure 6. Fgfr2Δ/Δ lenses exhibit reduced Aquaporin0 expression and a nuclear retention phenotype that Pten deletion fails to rescue.
Cre-negative control (A, E), PtenΔ/Δ (B, F) , Fgfr2Δ/Δ (C, G) , and (Pten/R2)Δ/Δ (D, H) lenses were analyzed for Aquaporin0 protein expression at E15.5 (A–D) , and for denucleation by TUNEL at E18.5 (E–H) . Both Fgfr2Δ/Δ (compare C to A; J, K) and (Pten/R2)Δ/Δ (Compare D to A; J, K) lenses experienced a reduced Aquaporin0 expression level. Additionally, Fgfr2Δ/Δ (C) and (Pten/R2)Δ/Δ (D) contained several heightened areas of Aquaporin0 expression in a circular pattern (C and D white arrows). Aquaporin0 expression in PtenΔ/Δ lenses did not differ from controls (compare B to A; J, K). Western blot analysis was performed at E15.5 to confirm the reduced Aquaporin0 protein observed with FGFR2 deficiency (K). The western blot quantification was standardized to GAPDH protein. TUNEL analysis detected normal fiber cell DNA degradation in both control (E) and Pten deleted lenses (F). However DNA degradation in the central fiber cells was markedly reduced in both Fgfr2Δ/Δ (G) and (Pten/R2)Δ/Δ (H) lenses. Quantitative RT-PCR revealed a reduction in trancripts for DnaseIIβ at E16.5 (I). The quantification of DnaseIIβ was standardized to GADPH mRNA. Reduced transcript levels of DnaseIIβ were observed in Fgfr2Δ/Δ and (Pten/R2)Δ/Δ lenses (I). PtenΔ/Δ lenses did not display defects in Aquaporin0 protein expression (J)/localization (B), nuclear removal (F), or DnaseIIβ expression (I). White arrows point towards heightened and abnormal expression of Aquaporin0 in C and D, and TUNEL foci in E, F, and H. Errors bars on the graphs represent s.e.m, with each bar representing a minimum of 9 measurements (3 sections from the lens center of 3 different embryos). Scale bars: 200 μm in A–D; 100 μm in E–H.