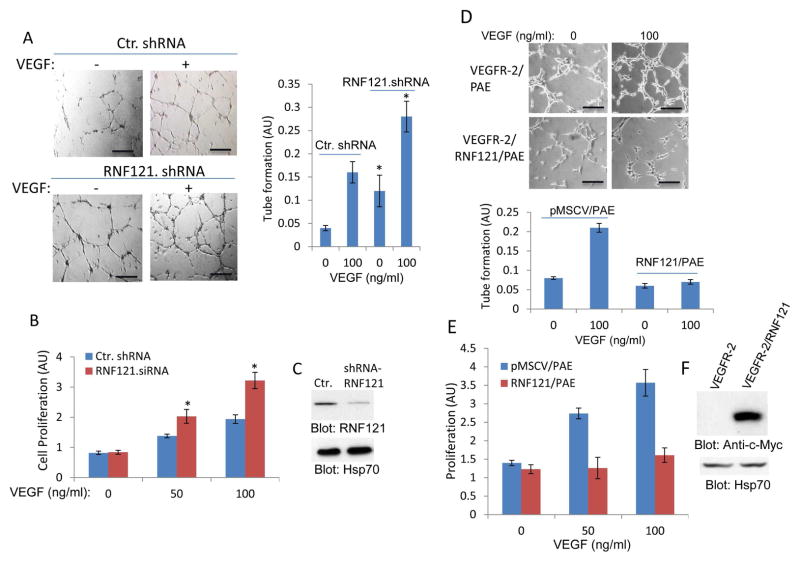
Figure 6. RNF121 inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis.
(A) Human primary umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) that were infected with control shRNA or with RNF121 shRNA were plated on the matrigel coated 24-well plates and stimulated with VEGF or control medium containing 2% FBS. Capillary tube formation of HUVECs viewed under microscope after 12 hours and pictures were taken with camera attached to microscope. Scale bars, 100 μm. Capillary tube formation of HUVECs was quantified using NIH Image J program. Graph is representative of capillary tube formation of HUVECs infected with control and RNF121 shRNA (three randomly selected fields per group were used for quantification). *p< 0.05, n=3 compared to control cells expressing control shRNA. (B) HUVECs infected with control shRNA or with RNF121 shRNA were subjected to proliferation assay using MTT solution as described in the Materials and Method section. *p< 0.05, n=3 compared to control cells without VEGF stimulation. (C) Shown is the silencing effect of RNF121 shRNA on the expression of RNF121. (D) PAE cells expressing VEGFR-2 alone or co-expressing VEGFR-2 with RNF121 were subjected to matrigel angiogenesis assay as panel A and tube formation was quantified in a similar manner. Scale bars, 100 μm. (E) Proliferation of cells was measured by using MTT assay as panel A. (F) Ectopic expression of RNF121 in PAE cells is shown. Experiments (D–E) are representative of three independent experiments.