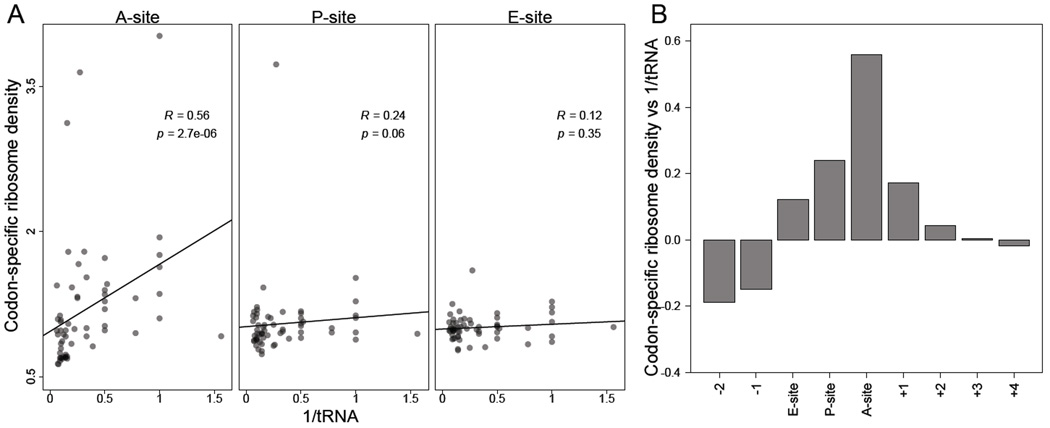
Figure 2. Codons corresponding to lower-abundance tRNAs are decoded more slowly.
(A) Correlation between codon-specific excess ribosome densities and cognate tRNA abundances. Codons within RPFs were assigned to the A-, P-, and E-site positions based on the distance from the 5' ends of fragments, and codonspecific excess ribosome densities were calculated (vk, Eqn S19). Cognate tRNA abundances for each codon were estimated using the genomic copy numbers of iso-accepting tRNAs and wobble parameters (Table S2). Spearman R values are shown, with their significance (p values).
(B) The correlations of codon–tRNA abundance at different positions relative to the A site. Analysis was as in (A) using varying offsets from the A-site position within RPFs (x axis) to calculate Spearman correlations (y axis).
See also Figures S2–3 and Tables S1–2.