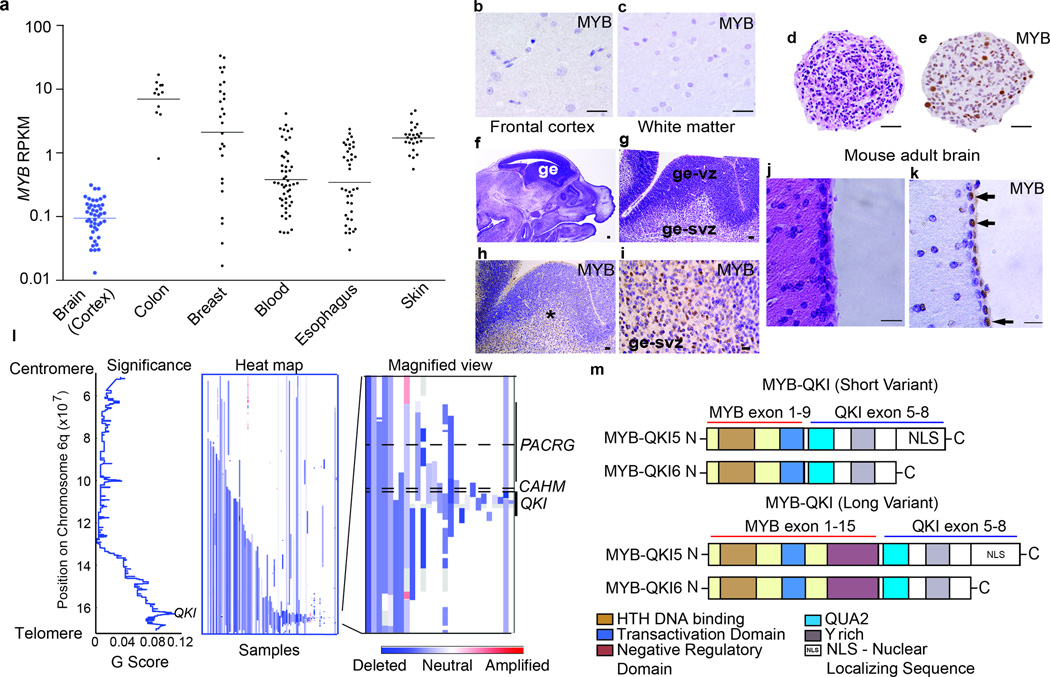
Figure 2. Alterations of MYB and QKI occur frequently in human cancers.
a. MYB expression (mean ± SEM) in normal human colon (n=12), breast (n=27), whole blood (n=51), esophagus (n=38), skin (n=25), and brain cortex (n=47).
b. MYB immunohistochemistry on human adult frontal cortex. Scale bar = 100 microns
c. MYB immunohistochemistry on human adult white matter. Scale bar = 100 microns
d. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) on human fetal neural stem cells generated from the ganglionic eminence at 22 weeks gestation. Scale bar = 100 microns
e. MYB immunohistochemistry demonstrates positive staining in a subset of cells. Scale bar = 100 microns
f. Sagittal section from embryonic 14.5 days post coitus (E14.5) mouse brain. Scale bar = 500 microns.
g. H&E of E14.5 ganglionic eminence (ge) including ventricular (ge-vz) and subventricular (ge-svz) zones. Scale bar = 50 microns.
h. MYB immunohistochemistry on the E14.5 ganglionic eminence. Scale bar = 50 microns.
i. MYB immunohistochemistry demonstrates positive staining in subventricular zone (ge-svz) but not the ventricular zone (ge-vz). Scale bars = 50 microns.
j. H&E from periventricular region of adult mouse brain. Scale bar = 100 microns.
k. Immunohistochemistry for MYB demonstrates positive cells (arrows) in the ependymal/SVZ layer. Scale bars = 100 microns.
l. (Left) Significance of deletions (x-axis) and (middle and right) heatmaps indicating copy-number profiles at 6q of individual adult Glioblastomas.
m. Structure of the MYB-QKI fusion protein. TAD denotes transactivating domain. C-terminus of QKI includes QUA2 domains. MYB-QKI5 retains a nuclear localizing sequence (NLS). Two variants of MYB-QKI are depicted corresponding to the breakpoint of MYB.