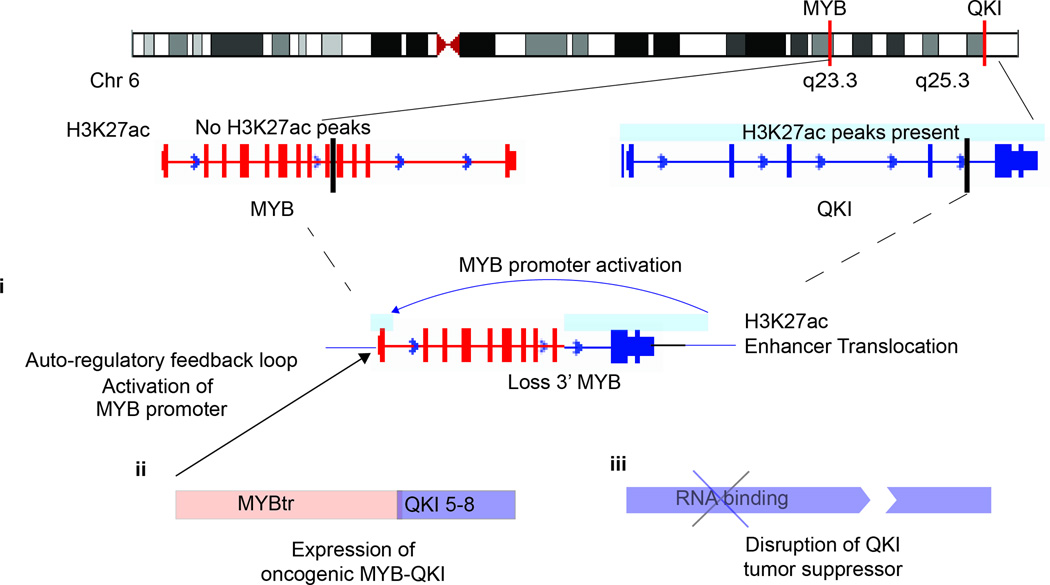
Figure 8. The MYB-QKI rearrangement contributes to oncogenesis through at least three mechanisms.
The MYB-QKI rearrangement disrupts both MYB and QKI, resulting in hemizygous deletion of 3’MYB and 5’ QKI. This results in proximal translocation of H3K27ac enhancers on 3’QKI towards the MYB promoter, resulting in MYB promoter activation (i). The MYB-QKI fusion protein that is expressed is oncogenic, functions as a transcription factor, and exhibits the ability to bind to and activate the MYB promoter, resulting in an auto-regulatory feedback loop (ii). Hemizygous loss of QKI results in suppression of QKI expression, which functions as a tumor suppressor gene (iii).