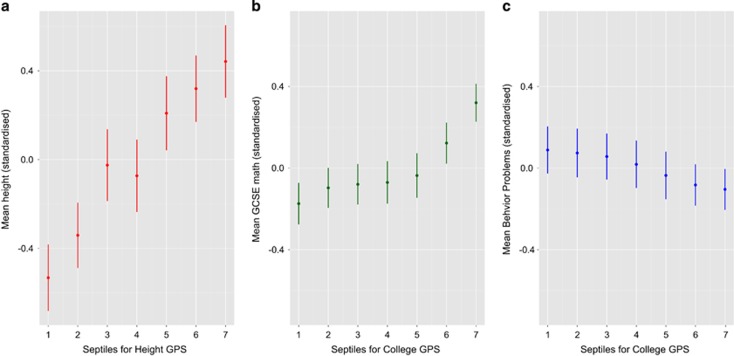
Figure 2.
(a) Mean for height at age 16 by adult Height genome-wide polygenic score (GPS) septile. The threshold for selecting trait-associated alleles was PT < 0.30. The GPS were converted to quantiles (1=lowest, 7=highest GPS). Mean phenotypic values and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the quantile groups (bars) were estimated using general linear regression with ancestrally informative principal components, sex and age of measurement as covariates. (b) Mean for children's mathematics educational achievement at age 16 (compulsory subject on the General Certificate of Secondary Examination (GCSE), see Materials and Methods for details) by College GPS septile. The threshold for selecting trait-associated alleles was PT < 0.30. The GPS were converted to quantiles (1=lowest, 7=highest GPS). Mean phenotypic values and 95% CI for the quantile groups (bars) were estimated using general linear regression with ancestrally informative principal components, sex and age of measurement as covariates. (c) Mean for total parent-reported behavior problems at age 16 by adult College GPS septile. The threshold for selecting trait-associated alleles was PT < 0.30 (the best-fit GPS as estimated by PRSice software, see Materials and Methods). The GPS were converted to quantiles (1=lowest, 7=highest GPS). Mean phenotypic values and 95% CI for the quantile groups (bars) were estimated using general linear regression with ancestrally informative principal components, sex and age of measurement as covariates.