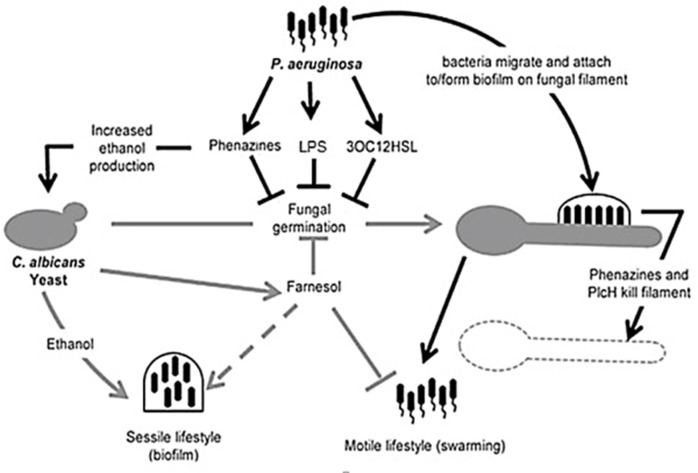
Figure 5.
Illustration of competition between Candida albicans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pseudomonas aeruginosa attaches to C. albicans hyphae and kills hyphal cells through secreted hydrolytic enzymes such as hemolytic phospholipase C (PlcH) and phenazines such as pyocyanin and 5-methylphenazine-1-carboxylic acid (5-MPCA). 3-oxo-homoserine lactone produced by P. aeruginosa and phenazines inhibit filamentation by C. albicans, similar to farnesol, produced by C. albicans. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inhibits C. albicans filamentation. Ethanol production is increased by the fungus, inhibiting the motility of P. aeruginosa (adapted from Lindsay and Hogan, 2014).