Figure 5.
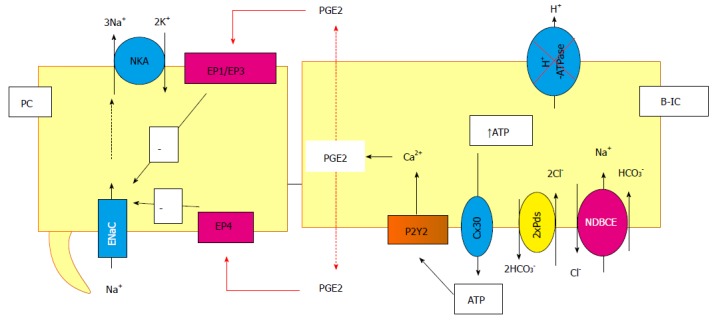
Cross-talk between principal and intercalated cells, example of the inhibition of the vacuolar proton pump. In this particular situation, the ATP is released by the B-intercalated in the lumen cell through connexion and then binds and activates the P2Y2 receptors. This activation leads to prostaglandin (PGE2) synthesis and release in both side of the cells. It binds to the EP receptors in principal cells, inducing, then, the inhibition of the Na+ reabsorption. NDBCE: Na+-driven bicarbonate/Cl- exchanger; PGE2: Prostaglandin; B-IC: Type B intercalated cells.
