Fig. 1.
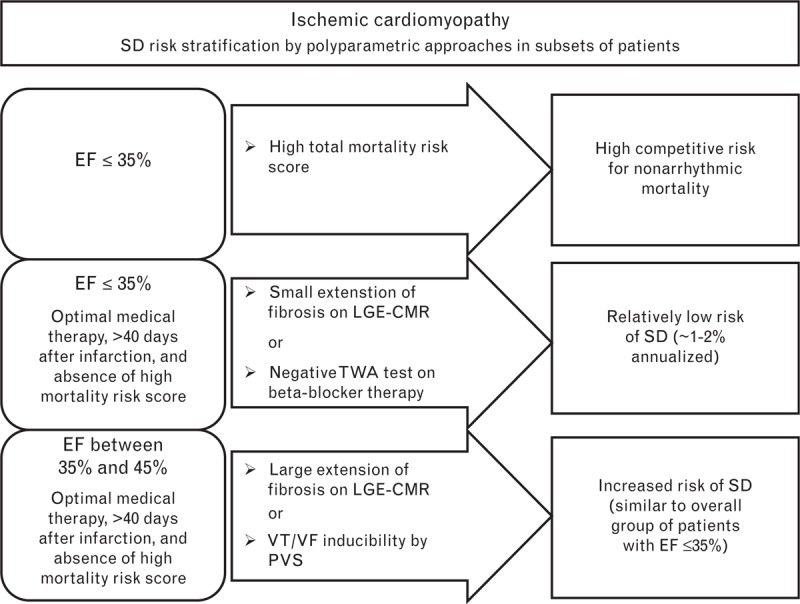
Sudden arrhythmic death risk stratification in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. The risk of sudden arrhythmic death was stratified according to ejection fraction, total mortality risk score, and the results of specific tests: late gadolinium enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (LGE-CMR) or the T-wave alternans (TWA) test in patients with ejection fraction of 35% or less, and LGE-CMR or programmed ventricular stimulation (PVS) in patients with ejection fraction between 35 and 45%. In ischemic cardiomyopathy, LGE is present in almost all patients; negative and positive LGE-CMR results are related to the presence of a small and large extent of ventricular fibrosis, respectively. The TWA test is considered negative only if it is performed under β-blocker therapy. The PVS test is considered positive if sustained ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation is inducible. EF, ejection fraction; LGE-CMR, late gadolinium enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; PVS, programmed ventricular stimulation; SD, sudden arrhythmic death; TWA, T-wave alternans; VF, ventricular fibrillation; VT, ventricular tachycardia.
