FIGURE 1.
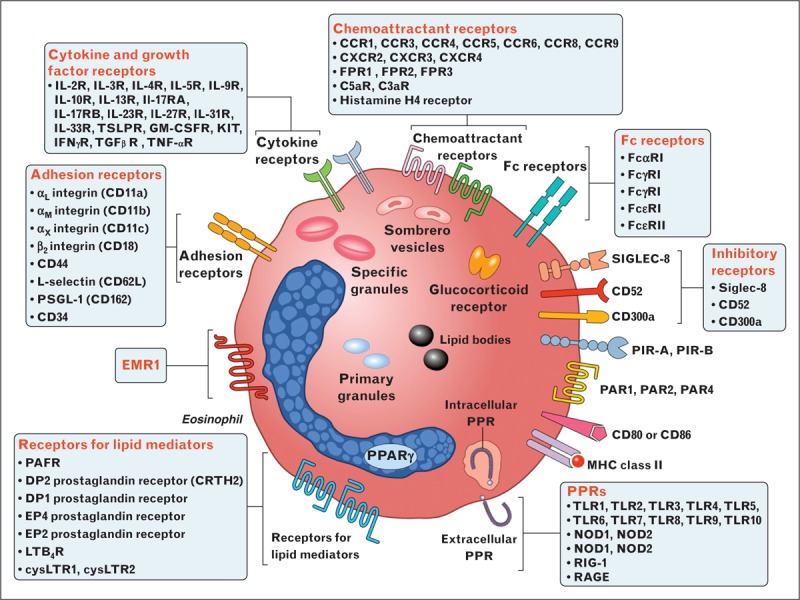
Human eosinophils display a wide spectrum of surface receptors that are important for their pleiotropic functions. Eosinophils express cell-surface receptors for cytokines and growth factors, chemokines, adhesion molecules, lipid mediators, chemoattractants, complement, immunoglobulins, Siglecs, histamine, PIRs, PARs, PPRs, CD40, CD80/CD86, and MHC class II. The epidermal growth factor-like module containing mucin-like hormone receptor 1 (EMR1) appears truly eosinophil specific [17]. Eosinophils contain the glucocorticoid receptor in high copy number [19]. The α variant of the glucocorticoid receptor is five-fold higher in eosinophils than in neutrophils making these cells highly susceptible to the therapeutic effects of glucocorticoids. Eosinophils contain specific granules containing several cationic proteins, primary granules, lipid bodies, and sombrero vesicles. CC, chemokine ligand; CCR, CC-chemokine receptor; CXCL, CXC-chemokine ligand; CXCR, CXC-chemokine receptor; PIRs, paired immunoglobulin-like receptors; PARs, proteinase-activated receptors; PPRs, pattern-recognition receptors.
