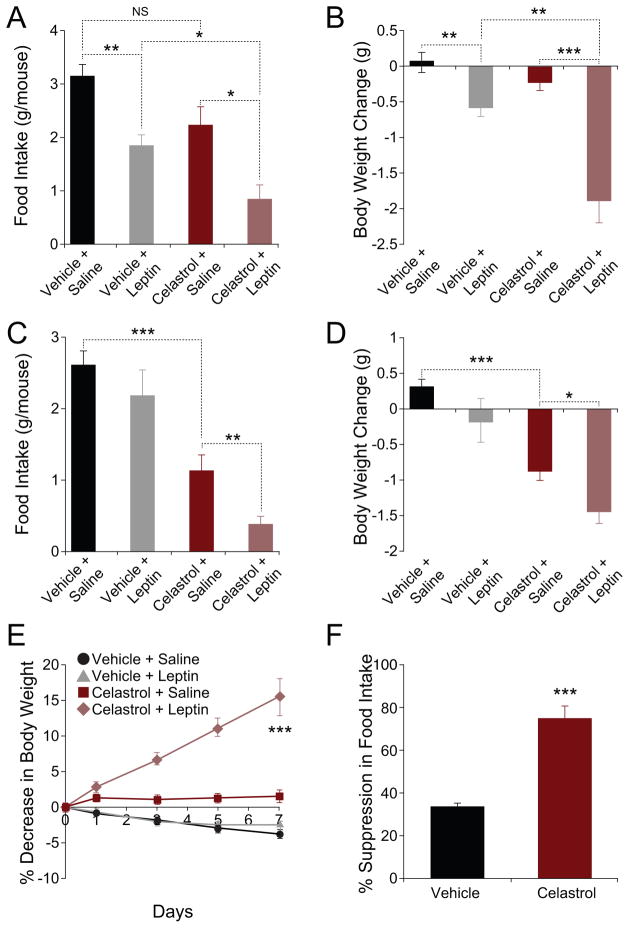
Figure 5. Celastrol Acts as a Leptin Sensitizer.
(A and B) Vehicle or Celastrol (150 μg/kg) were administered to lean mice for two days and each group was subsequently received either saline (n=9 for vehicle and n=11 for Celastrol subgroup) or leptin (n=12 for each subgroup) (5 mg/kg). (A) Food intake and (B) body weight change during 24-hour period following saline/leptin injections. Experiments were repeated in two independent cohorts. (C and D) Vehicle (n=12) or Celastrol (n=10; 150 μg/kg) were administered to DIO mice for two days and each group of mice was received either saline (n=6 vehicle; n=5 Celastrol) or leptin (n=6 vehicle; n=5 Celastrol) (1 mg/kg). (C) Food intake (g) and (D) body weight change (g) during 16-hour period following saline/leptin injections. These experiments were independently repeated two times. (E and F) ob/ob mice were treated with either vehicle (n=9) or Celastrol (100 μg/kg, n=9) for the next five days. For the next one week, each group of mice was also treated with either saline or leptin (0.1 mg/kg) (n=5 saline and n=4 leptin). (E) Percent decrease in body weight. (F) Percent suppression of food intake during leptin treatment. Experiments were repeated in two independent cohorts. Error bars are represented as mean ± SEM. p values were determined by Student’s t test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).