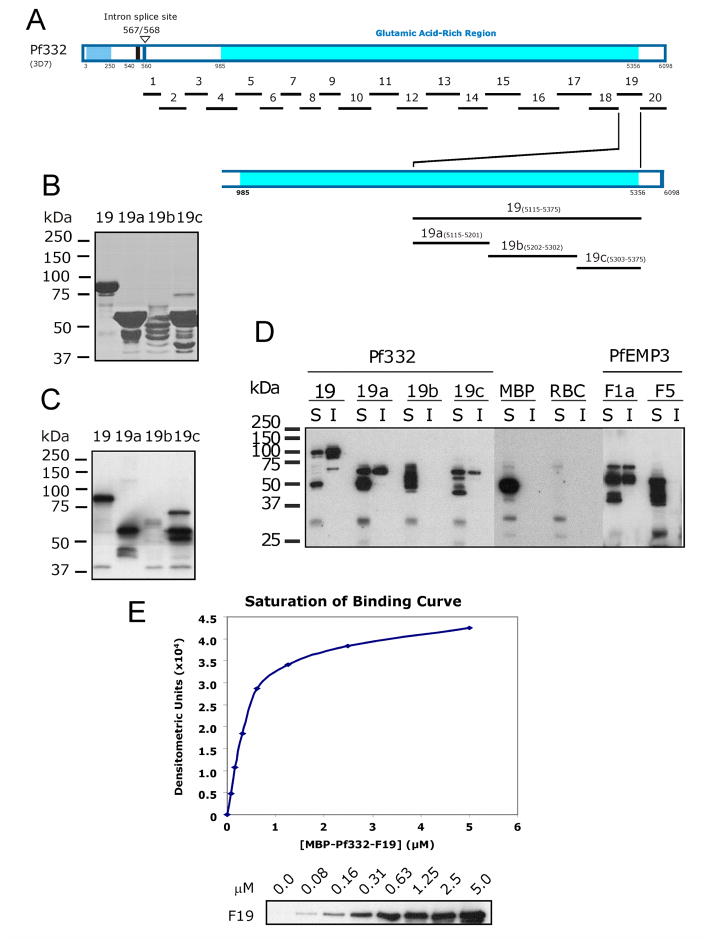
Fig. 3. Finer mapping of residues in Pf332-F19 that bind to the Membrane Skeleton.
A. Schematic representation of full length Pf332 protein showing the relative locations on the twenty fragments investigated. To further define the binding residues contained within the 260 residue –F19 region, three smaller non-overlapping sub-fragments (-F19a, -F19b and –F19c) were expressed and purified as MBP fusion proteins.
B. Purified MBP-Pf332 F19 sub-fragment fusion proteins. 2μg (total protein) of each purified protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE before staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue.
C. Each of the MBP-Pf332 F19 sub-fragment fusion proteins (50ng total protein) was immunoblotted with anti-MBP antiserum to confirm the presence of the N-terminal MBP tag and demonstrate the apparent molecular mass of each protein when immunoblotted.
D. The TX100 soluble (S) and insoluble (I) fractions of lysed and resealed RBCs that had been incubated with 5 μM fusion protein were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-MBP antiserum. MBP-Pf332-F19, and its sub-fragment proteins –F19a and –F19c were both detected in the Tx100 soluble and insoluble fractions, whereas the intervening sub-fragment –F19b was not. Neither MBP nor MBP-PfEMP3-F5 was detected in the insoluble fractions, whereas MBP-PfEMP3-F1a was. Together, these data map a membrane skeleton binding region of Pf332 to the 86 residues of –F19a. These data also suggest the presence of other residues within the downstream 72 residues of –F19c that may contribute to the overall protein interaction of Pf332 with the membrane skeleton.
E. A saturation of binding curve was constructed from the densitometric data obtained from a representative IOV binding assay using serial dilutions of MBP-Pf332-F19 protein (titrated from 5.0 to 0.0 μM; panel below the graph). The half saturation concentration (Kd) was determined to be Kd = 0.40 μM.