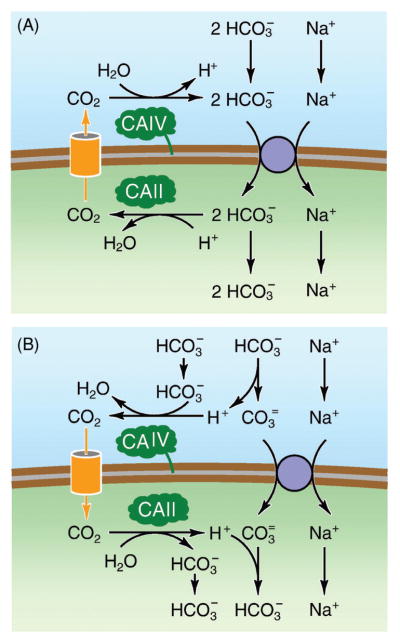
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram showing the rationale for determination of whether HCO3− or CO3 2− is the transported ion. It has been suggested (38, 292) that it is possible to distinguish between HCO3− and CO3 2− transport by measuring pH in the extracellular space near the membrane following a sudden change in transport activity, before and after inhibition of the carbonic anhydrase. If CO3− is the transported species an exaggerated decrease in pH would develop when the carbonic anhydrase is inhibited, while if HCO3− is the transported species a blunted decrease in pH would be the result. From (38).