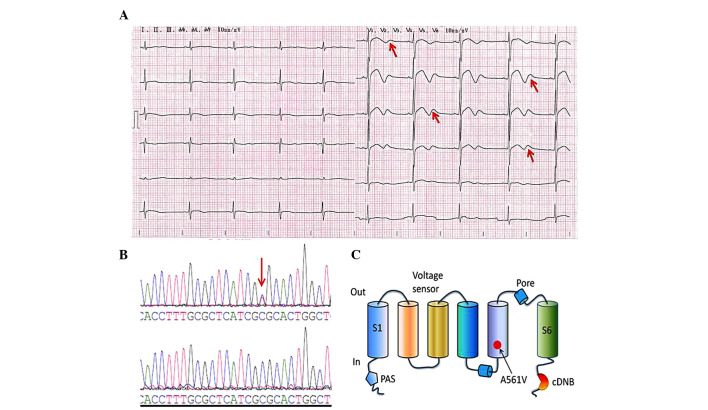
Figure 1.
ECG and mutation analysis. (A) ECG of the LQTS patient. The 12-lead ECG revealed a prolonged heart rate-corrected QT interval and biphasic T waves (indicated by the red arrows). (B) DNA sequencing chromatogram demonstrating a heterozygous point mutation, 1682C→T in the hERG gene of the LQTS patient (upper DNA sequencing chromatogram) and DNA sequence analysis in a healthy individual (lower DNA sequencing chromatogram); the red arrow indicates the mutation site. (C) This mutation leads to the substitution of the amino acid, alanine (A) by valine (V) in the S5/pore region of the hERG protein (A561V). ECG, electrocardiogram; LQTS, long-QT syndrome; hERG, human ether-à-go-go-related gene; cDNB, cyclic-nucleotide-binding domain.