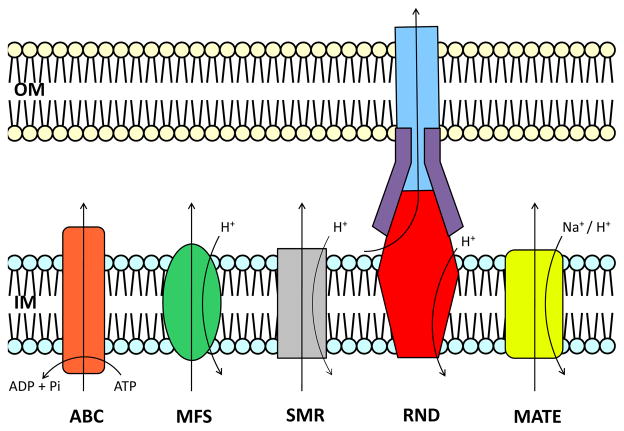
Fig. 1. Functional diversity among efflux proteins.
Based on mode of transport, energy coupling mechanism and phylogeny (104, 105) these proteins are divided into five superfamilies. The ABC (left) superfamily proteins utilize ATP to transport diverse antimicrobials across the cellular inner-membrane. SMR, MFS and RND proteins function via a H+-substrate antiport mechanism. MATE proteins have been found to utilize both H+ and Na+ as an energy source (106). RND transporters, in particular, are capable of forming multi-protein structures which bridge the inner- and outer-membrane.