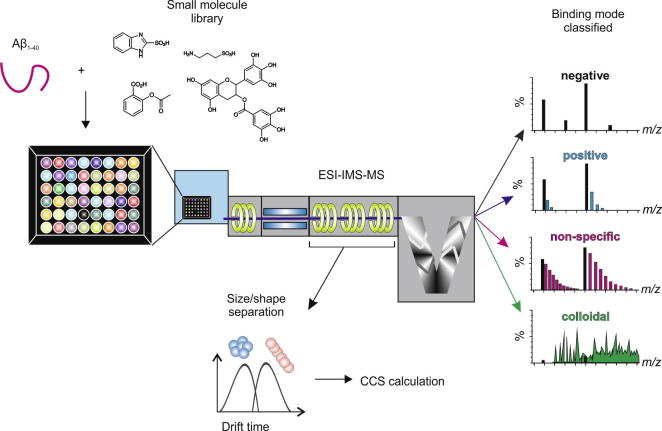
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the ESI-IMS–MS experimental procedure. The protein of interest is mixed individually with small molecules from a compound library in 96-well plate format. Via a Triversa NanoMate automated nano-ESI interface, the samples are infused into the mass spectrometer, wherein separation occurs based on the mass to charge ratio (m/z) and collisional cross-sectional area (CCS). A non-interacting small molecule will produce a spectrum the same as that generated by the peptide alone (black). A small molecule that specifically interacts with the peptide will produce a binomial distribution of bound peaks (blue) [45]. A non-specific ligand will bind but result in a Poisson distribution of bound peaks (pink) [45]. A colloidal inhibitor will produce a range of overlapping peaks due to self-association of the small molecule (green).