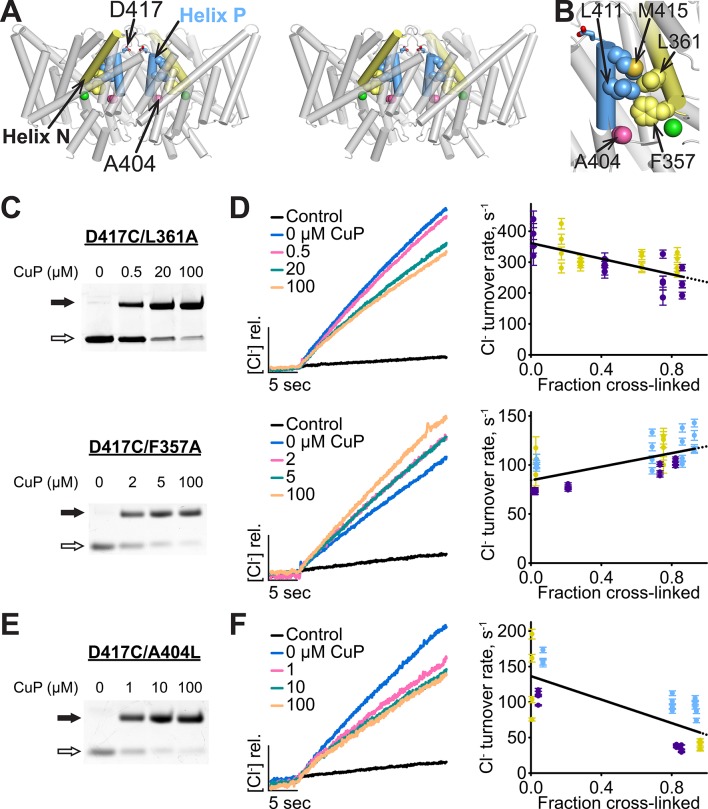
Figure 11. Helix P is coupled to the extracellular gate via Helix N.
(A) Side view of ClC-ec1, in stereo. Conserved residues L411 and M415 in Helix P (blue) make direct contact with conserved residues F357 and L361 in Helix N (yellow). (B) Close-up of Helices P and N. (C) Detection of inter-subunit disulfide cross-links by non-reducing SDS-PAGE in Helix-N mutants D417C/L361A (top) and D417C/F357A (bottom). (D) Effect of cross-linking on activity. Left: Representative data traces showing Cl--transport activity of D417C/L361A and D417C/F357A. Right: Summary data showing Cl--transport activity as a function of disulfide cross-linking. Each data point represents individual data points as described in Figure 4. Purple, yellow and blue each represent data obtained from a separate protein preparation. (E) Detection of inter-subunit disulfide cross-links on D417C/A404L (F) Effect of cross-linking on activity of D417C/A404L. Purple, yellow and blue represent data obtained from separate protein preparations.