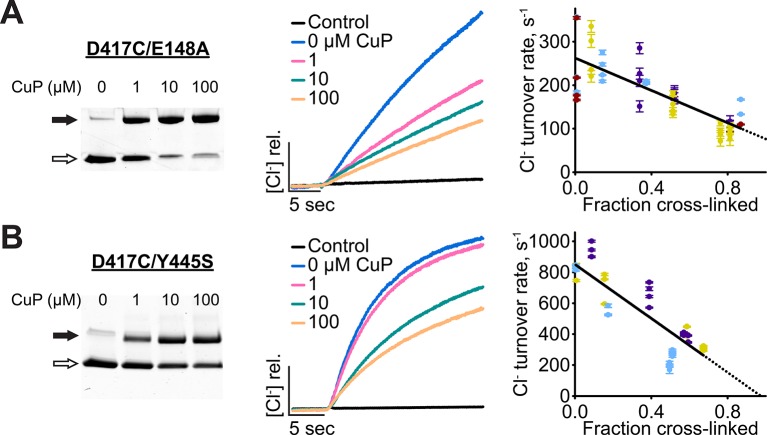
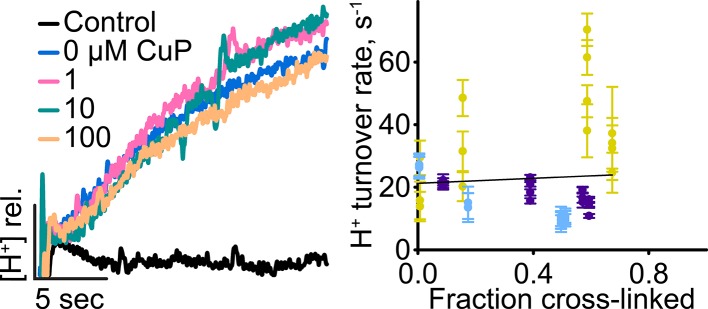
Figure 6. Cross-linking D417C in uncoupled transporter backgrounds.
(A) D417C/E148A – detection of inter-subunit disulfide cross-links by non-reducing SDS-PAGE. (B) Effect of cross-linking on activity of D417C/E148A. Left: Representative data traces showing Cl--transport activity. Right: Summary data showing Cl--transport activity as a function of disulfide cross-linking. Each data point represents one flux-assay measurement, with error bars indicating the uncertainty in curve-fitting to the primary data. Purple, yellow, blue, and dark red each represent data from a separate protein preparation. (C) D417C/Y445S – detection of inter-subunit disulfide cross-links. (D) Effect of cross-linking on activity of D417C/Y445S, as in panel B. Data are from three separate protein preparations (indicated in purple, yellow, and blue).