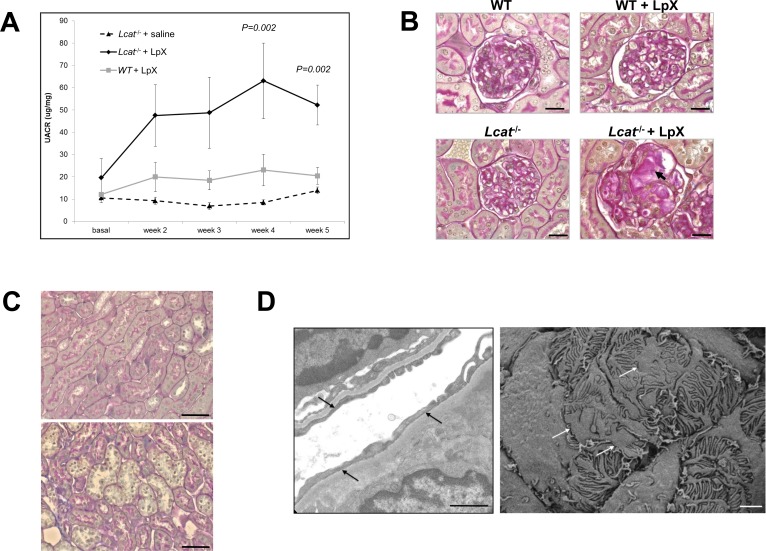
Fig 5. LpX induces nephropathology in Lcat-/- mice.
(A) Effect of LpX injection on renal function. Albumin to creatinine ratios (μg/mg) in urine (UACR) were measured prior to and then every week after exogenous LpX treatment, starting on week 2. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. P values of group differences at each time point are reported. (B) Histological analysis. Representative images of PAS-stained sections of kidneys from WT and Lcat-/- mice treated or not treated with LpX. No histological alterations were present in WT mice. WT mice treated with LpX showed no changes or only mild mesangial matrix expansion. In Lcat-/- mice, LpX treatment increased mesangial matrix (asterisk) and, occasionally, PAS-positive material in glomerular capillaries (arrow) was observed (Scale bars: 20 μm). (C) Representative images of PAS-stained sections of kidneys from WT (upper panel) and Lcat-/- (lower panel) mice treated with LpX. Tubular cell vacuolation was present focally in Lcat-/- mice. (Scale bars: 50 μm). (D) Podocyte effacement revealed by TEM (left, black arrows; Scale bar: 1 μm) and SEM (right, white arrows; Scale bar: 20 μm) in glomeruli of Lcat-/- mice treated with LpX.