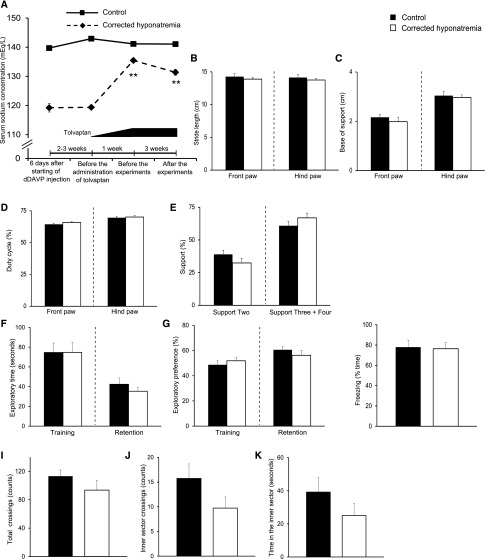
Figure 9.
Gait and memory performances of corrected hyponatremic rats were equivalent to those of control rats suggesting that chronic hyponatremia-induced behavioral abnormalities are reversible. (A) Serum sodium concentration of control (n=14) and corrected hyponatremic (n=13) rats. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test; **P<0.01 versus corrected hyponatremia on day 6. (B–E) Quantitative analysis of footprint patterns in control (n=8) and corrected hyponatremic (n=8) rats; (B) stride length; (C) base of support; (D) duty cycle and (E) support. (F and G) Performance of novel-object recognition tests (NORTs) in control (n=11) and corrected hyponatremic (n=11) rats; (F) exploratory time; (G) exploratory preference. (H) The freezing performance of control (n=11) and corrected hyponatremic (n=11) rats in contextual fear conditioning tests. (I–K) Performance of control (n=11) and corrected hyponatremic (n=11) rats in open field tests; number of (I) total and (J) inner sector crossings, and (K) time in the inner sector. Student’s t test.