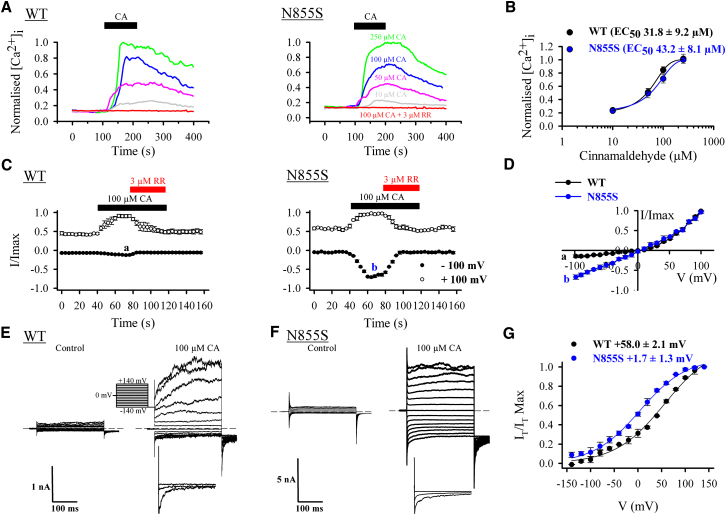
Figure 4.
Pharmacological and Biophysical Analysis of hTRPA1-WT and hTRPA1-N855S
(A) Intracellular calcium response to 250 μM, 100 μM, 50 μM, and 10 μM CA and to 100 μM CA in the presence of 3 μM ruthenium red (RR). Results for HEK293 cells expressing hTRPA1-WT are shown on the left and for hTRPA1-N855S on the right. Horizontal bars at the top indicate the time of CA application.
(B) Dose-response curve of CA-evoked calcium responses for hTRPA1-WT and hTRPA1-N855S. [Ca2+]I normalized to maximum calcium response to 250 μM CA. Traces represent average [Ca2+]I from 20–30 cells. Data were fit to the Hill equation.
(C) HEK293 cells expressing hTRPA1-WT (left; n = 5) or hTRPA1-N855S (right; n = 6) show activation by CA (100 μM) and inhibition by ruthenium red (RR). Currents were recorded at +100 mV and –100 mV and are normalized to current at +100 mV. Letters denote time point at which voltage ramps (shown in D) were acquired to generate current-voltage relationships.
(D) Average current-voltage relationship of hTRPA1-WT and hTRPA1-N855S in the presence of 100 μM CA. Currents are normalized to +100 mV.
(E) Whole-cell current traces of HEK293 cells expressing hTRPA1-WT in response to the indicated voltage step protocol in the absence (left) and presence (right) of 100 μM CA. Bottom panel shows higher resolution of normalized tail current in response to a step to −140, 0, and +140 mV. Dotted line shows zero current level.
(F) Same as (E) but in HEK293 cells expressing hTRPA1-N855S.
(G) Mean steady-state activation curves obtained from tail currents (IT) at −140 mV for hTRPA1-WT (n = 5) and hTRPA1-N855S (n = 6) in the presence of CA. The midpoints of voltage activation (V1/2) for the WT and mutant channels are indicated at the top. Error bars in all plots represent SEM across individual cell measurements.