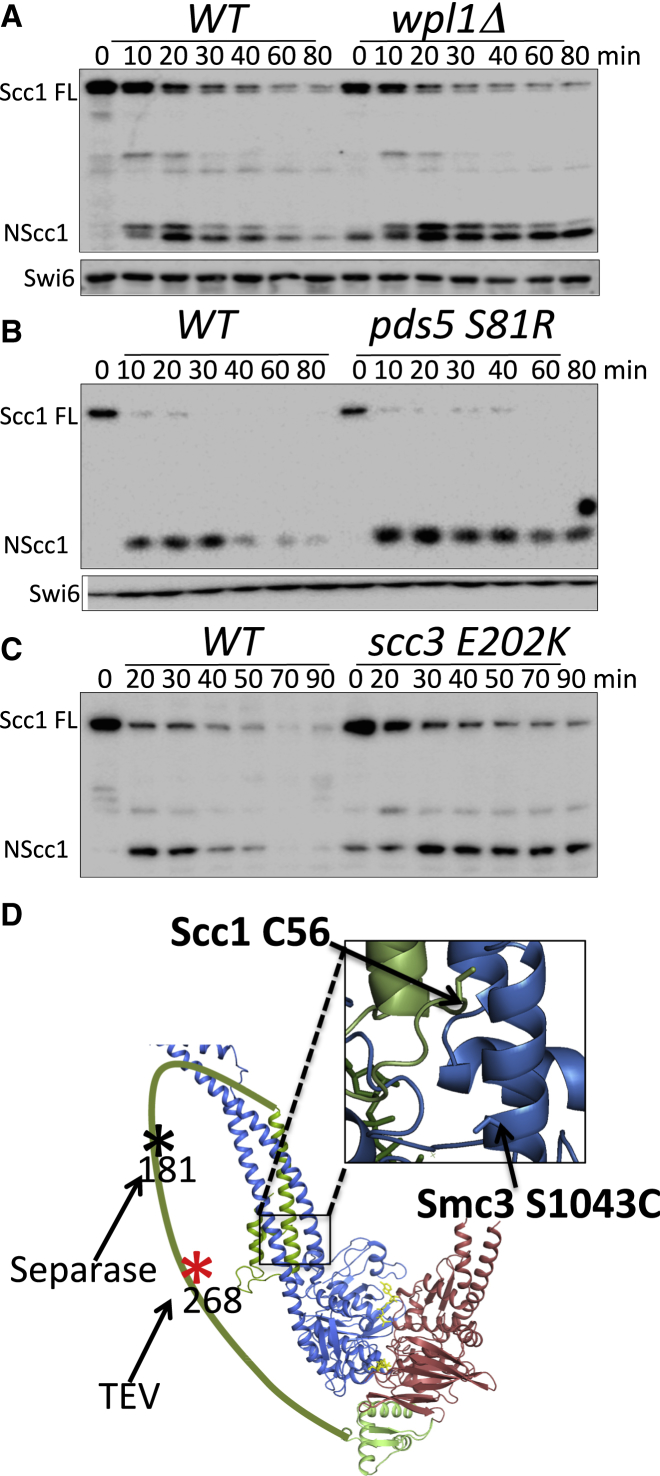
Figure 1.
Stability of Scc1 Cleavage Fragments in Releasing Activity Mutants
(A–C) Wild-type (K17960), wpl1Δ (K20236), pds5-S81R (K20521), and Scc3-E202K (K20526) strains expressing CDC20 from the GAL promoter were grown to logarithmic phase at 25°C in YP medium containing galactose, transferred to galactose-free media to induce metaphase arrest (time 0), and anaphase triggered by galactose readdition. Separase cleavage of Scc1 was followed by western blotting, detecting N-terminal Myc tag on Scc1.
(D) Model of the ATPase domains of Smc1 and Smc3 in an engaged state driven by ATP binding. The separase cleavage site in Scc1 at position 181 is marked with a black asterisk; TEV sites at position 268 are marked with a red asterisk.