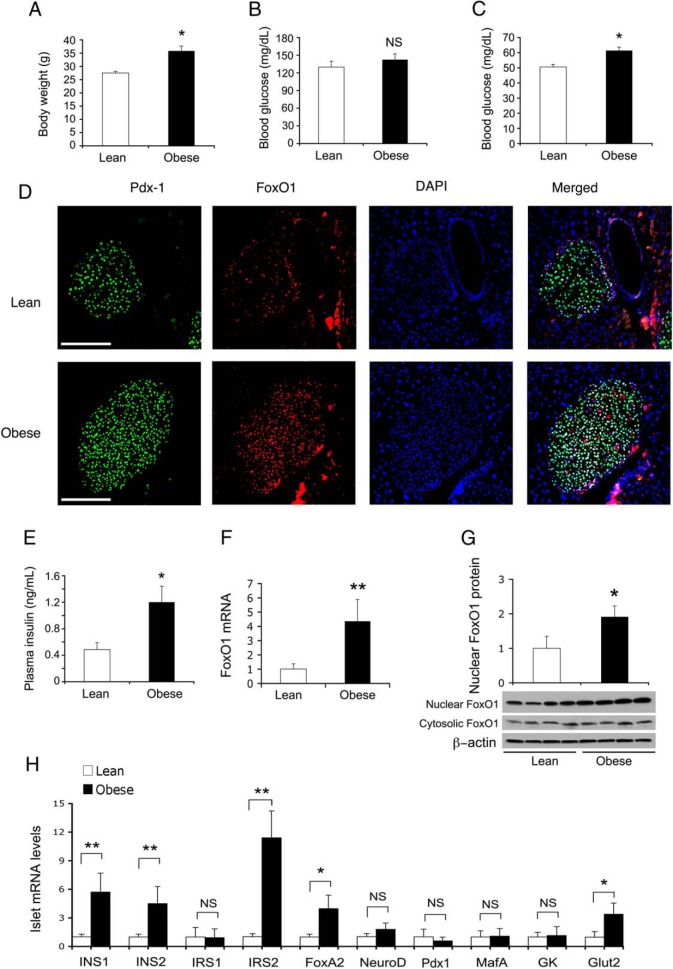
Figure 4.
FoxO1 contributes to physiological β-cell compensation for insulin resistance in obese mice. C57BL/6J mice (male, 6 wk old, n = 7/group) were fed regular chow or high-fat diet for 10 weeks, followed by determining body weight and blood glucose metabolism. A, Body weight. B, Fed blood glucose levels. Fed blood glucose levels were determined in mice under ad libitum condition. C, Fasting blood glucose levels. Fasting blood glucose levels were determined after a 16-hour fasting. D, Immunohistochemistry of pancreas for visualizing Pdx1 and FoxO1 proteins in islets. E, Fasting plasma insulin levels. Mice were fasted for 16 hours for determining fasting plasma insulin levels. F, FoxO1 mRNA levels in islets. G, FoxO1 protein levels in islets. H, Islet mRNA levels. Mice were killed at 17 weeks of age for isolating islets. Handpicked islets (150–200 islets per mouse) were subjected to real-time qRT-PCR analysis using 18S RNA as control or immunoblot assay using β-actin as control for determining FoxO1 and β-cell mRNA levels as well as FoxO1 nuclear vs cytoplasmic protein levels. *, P < .05 and **, P < .001 vs control. NS, not significant. Scale bar, 50 μm.