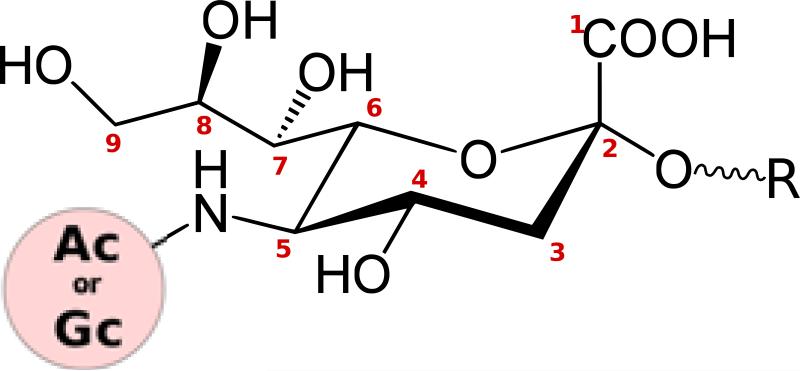
Fig. 1. Structure and diversity of sialic acids.
The core structure of sialic acid comprises a pyranose ring and a glycerol tail. The 5-carbon position can carry an N-Acetyl (Ac) or N-Glycolyl (Gc) group. Several types of O-substitutions have been discovered at carbon positions 4, 7, 8, and 9, giving rise to an enormous diversity of sialic acids. Carbon 2 forms glycosidic linkages with various sugars (R).