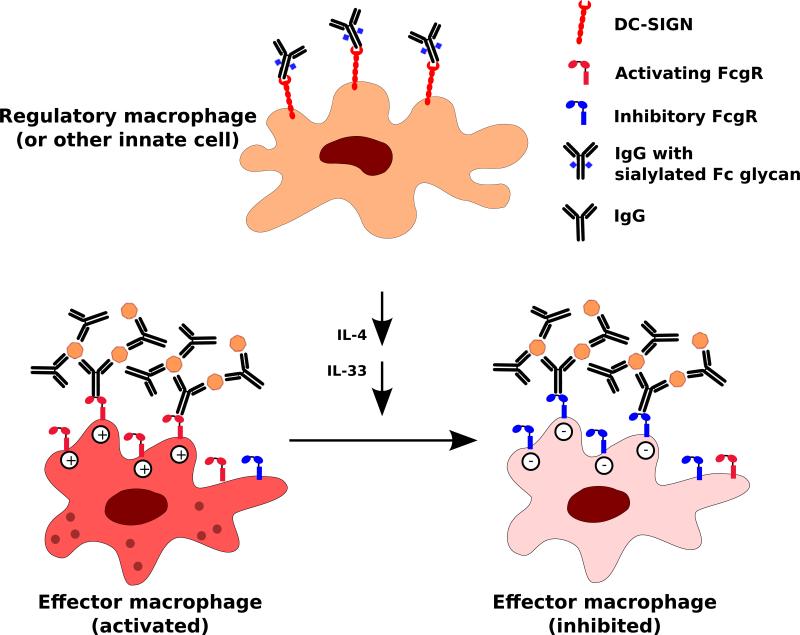
Fig. 7. Immunodulatory role of Fc glycan sialylation.
IgGs with sialylated Fc glycans engage DC-SIGN on regulatory macrophages or other innate immune cells. This interaction, via a cascade of events involving the production of secreted mediators such as IL-4, IL-33, alters the balance of activating and inhibitory FcγRs on effector macrophages. Signaling through inhibitory FcγRs predominates, resulting in the dampening of inflammation.