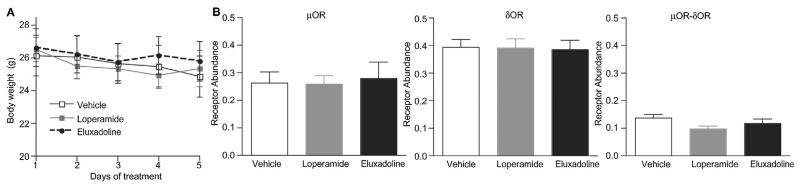
Fig. 7.
Effect of chronic treatment of loperamide and eluxadoline on body weight (A) and on receptor expression levels in ileal longitudinal muscle (B). Mice were treated with loperamide or eluxadoline (10 mg/kg, p.o., once a day for 5 days), or with 0.5% methylcellulose (0.1 ml/10 g; vehicle). (A) Body weight was measured immediately before the daily administration. Results are the mean ± S.E.M. n= 6–7. (B) On 6th day, ileum was collected (3–4 mice/sample). Membranes (10 μg) from mouse ileal longitudinal muscle (containing the myenteric plexus) were subjected to an ELISA assay in as described in Section 2. Tissues from 3 to 4 individual animals were pooled and collected as one sample. ELISA was performed in triplicate. Results are the mean ± S.E.M. n = 5.