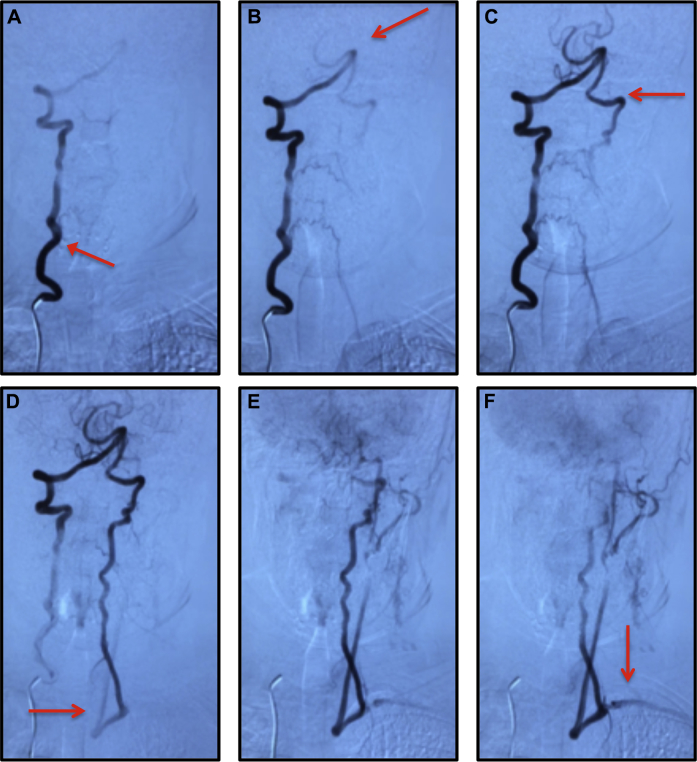
Fig. 1.
(A) Introduction of contrast and blood flow in the right vertebral artery (RVA, red arrow). (B) Continued flow through the RVA into the vertebral-basilar junction (red arrow). (C) Flow through the basilar artery (note the tortuous appearance); and the beginning of retrograde flow into the left vertebral artery (LVA, red arrow). (D) Continued retrograde flow through LVA with initial left common carotid artery (red arrow) flow. (E) Flow through the left common carotid artery, with bifurcation into the left internal and external carotid arteries. (F) Flow through the left external and internal carotid arteries. Note the delayed perfusion through the left subclavian artery (red arrow).