Fig. 5.
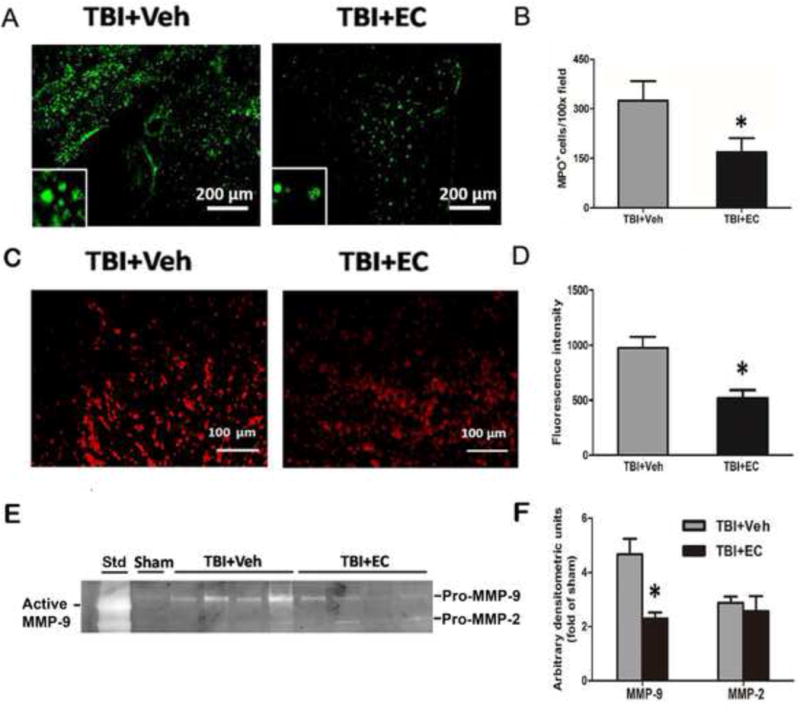
EC reduces TBI-induced neutrophil infiltration, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and MMP-9 enzyme activity. (A) Representative MPO immunoreactivity on brain sections from vehicle- and EC-treated groups on day 1 after TBI. (B) Quantification analysis showed that the EC-treated TBI group had less MPO-positive infiltrating neutrophils than did the vehicle-treated group. n=6/group, *p<0.05. (C) Mice were injected intraperitoneally with hydroethidine, which is oxidized to ethidium in the presence of superoxide. After TBI, ethidium fluorescent signal (seen as small red particles) was evident around the lesion in brain sections at 1 day. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Quantification analysis of fluorescence intensity indicated that ROS production was significantly less in the EC group than in the vehicle group at 1 day after TBI. n=6/group, *p<0.05 (t-test). (E) Representative gelatin gel zymogram of MMP-9 and MMP-2 activity at 3 days post-TBI. (F) Quantification analysis indicated that EC decreased MMP-9 activity, but not MMP-2 activity, compared with that in the vehicle-treated group. n=6/group, *p<0.05 (t-test).
