Fig. 7.
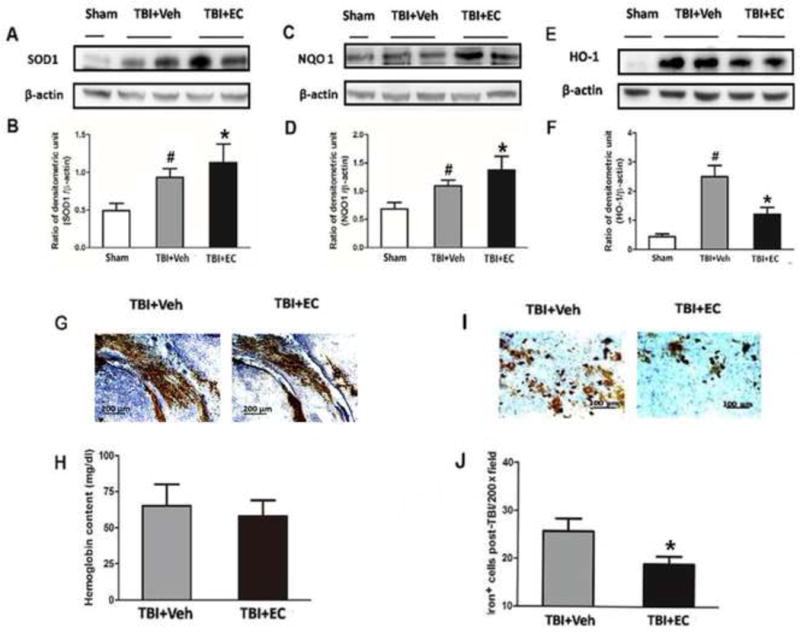
EC increases superoxide dismutase (SOD1) and quinone 1 (NQO1) expression and reduces heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) protein expression and iron deposition on day 3 post-TBI. (A–F) The upper panels show immunoblots of ipsilateral hemispheres 3 days after sham surgery or TBI. The lower panels represent the quantitative analysis. SOD1 and NQO1 expression each increased after TBI and were further increased in mice treated with EC. In the absence of EC, TBI significantly increased HO-1 expression compared with that in the sham group. EC treatment significantly prevented this increase. *p<0.05 versus vehicle group; #p<0.05 versus sham group (one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls test). (G) Images of bleeding in the injury area on day 3 post-TBI. (H) EC did not reduce brain hemoglobin level. n=6/group, p>0.05 (t-test). (I) Representative Perls-stained brain sections on day 3 post-TBI. (J) Quantification analysis showed that TBI mice treated with EC had fewer iron-positive cells in the injury area than did vehicle-treated mice. *p<0.05 (t-test).
