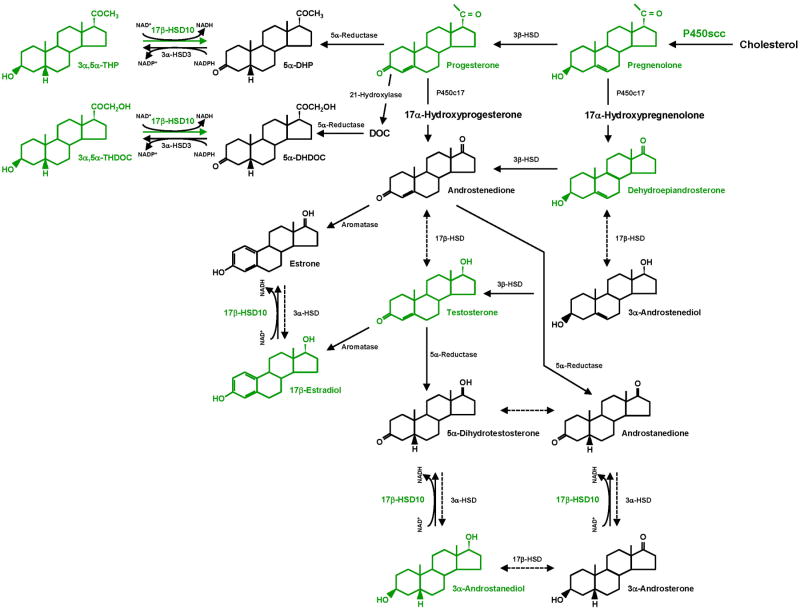
Figure 1.
Outline of neurosteroidogenesis. Neuroactive steroids and neurosteroidogenic enzymes that are potential key therapeutic targets are shown in green. The side chain of cholesterol is cleaved by P450scc as cholesterol is transported to the inner mitochondrial membrane and thus converted to pregnenolone. Soluble pregnenolone can enter into the endoplasmic reticulum unaided. 17β-HSD10 catalyzes the oxidation of neuroactive steroids in mitochondria with NAD+ as the coenzyme. This enzyme most effectively catalyzes the oxidation of 3α,5α-THP and 3α,5α-THDOC such that it is essential for the homeostasis of these neuroactive steroids, which was controlled by a dual enzyme molecular switch, composed of 17β-HSD10 and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type III (AKR1C2) localized in distinct subcellular compartments, mitochondria and ER, respectively (164, 168). The catalytic efficiencies (kcat/Km) of 17β-HSD10 are as high as 427 and 1,381 min-1 •mM-1 for the oxidation of 3α,5α-THP and 3α,5α-THDOC, respectively (163, 164). Abbreviations: 5α-DHP, 5α-dihydroprogesterone; DOC, deoxycorticosterone; 5α-DHDOC, 5α-dihydrodeoxycorticosterone; 3α,5α-THP, (3α,5α)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one or allopregnanolone; 3α,5α-THDOC, (3α,5α)-3,21-dihydroxypregnan-20-one or allotetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone; HSD, hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.