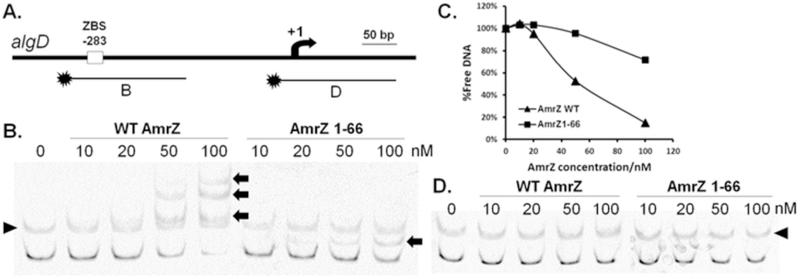
Figure 2. Truncation of the C-terminal domain results in reduced binding affinity to PalgD.
[6FAM]-labeled DNA fragments (10 nM in each reaction) with (B) or without (D) the ZBS in PalgD were incubated with various concentrations of AmrZ or AmrZ1-66 at room temperature for 20 min and resolved by 4% non-denaturing PAGE on ice (B. & D.). Relative amounts of free DNA in (B.) were quantified via densitometry of non-shift bands using ImageJ (v1.46r) and plotted against AmrZ concentrations (C.). AmrZ monomeric concentrations ranged between 10 nM and 100 nM. The arrow in (A.) represents the PalgD transcription start site. Arrows in (B.) indicate DNA mobility shifts induced by AmrZ or AmrZ1-66 binding. Triangles in (B. & D.) point to non-specific bands, which are also present in no protein lanes.