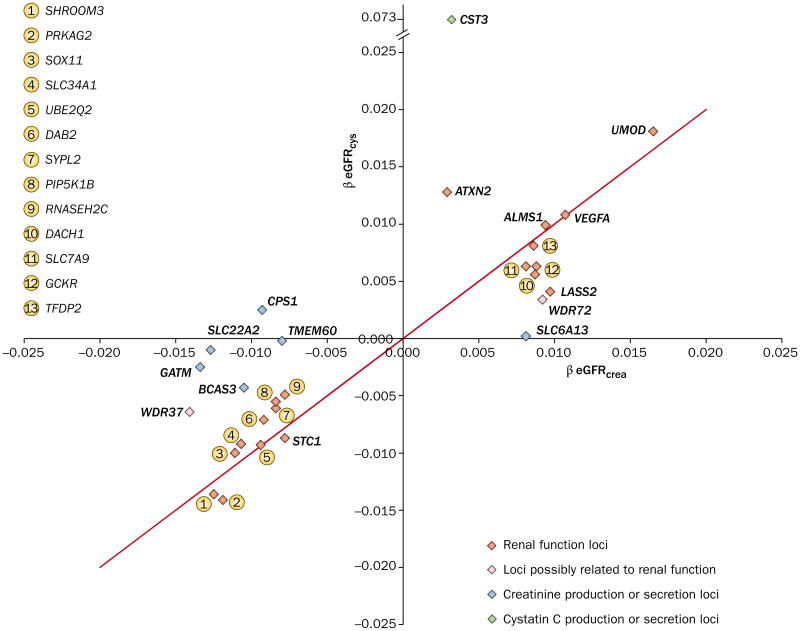
Figure 3.
Magnitude of association between GFR estimated from creatinine and cystatin C and SNPs identified in a GWAS of GFR and CKD. Loci lying along the red line are equally associated with both measures of kidney function (creatinine and cystatin C), which suggests that they are related to true GFR. Loci that lie along the x-axis or y-axis are predominantly associated with GFR estimated from creatinine (eGFRcrea) or cystatin C (eGFRcys), respectively. These loci are more likely to be related to genetic variability in the production of creatinine or cystatin C than to true GFR. Abbreviations: CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated GFR; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; GWAS, genome-wide association study; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism. Permission obtained from Nature Publishing Group © Köttgen, A. et al. Nat. Genet. 42, 376–384 (2010).