Figure 9.
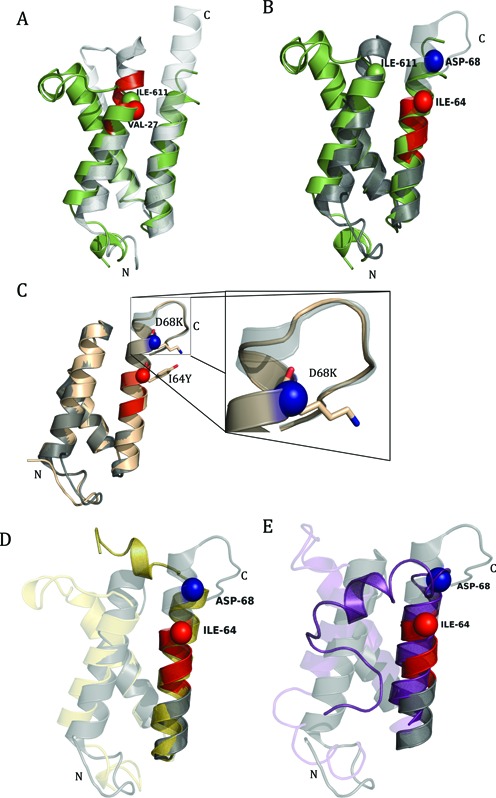
Junction-MoRF in human and yeast Med15 KIX domains. (A) Alignment of yeast Med15-KIX (gray) with human CBP-KIX (green). Yeast KIX structure was generated using PDB id 2K0N. Mutation at VAL-27 (red sphere) reduces the binding affinity of yeast Med15-KIX. VAL-27 aligns with ILE-611 (green sphere) which is the start of G2-loop in human CBP-KIX. (B) Alignment of human Med15-KIX (gray) with human CBP-KIX (green). KIX domain of human Med15 was generated using PDB id 2GUT. Residues ILE-64 (red sphere) and ASP-68 (blue sphere) play a role in maintaining the binding specificity of human Med15-KIX. (C) Alignment of mutated (I64Y and D68K) KIX (wheat) with human KIX (gray) domain. (D) Homology Model of Capsaspora owczarzaki CBP-KIX (yellow) aligned on human CBP-KIX (gray). (E) Homology model of Salpingoeca rosetta CBP-KIX (purple) aligned on Human CBP-KIX (gray). Homology models of C. owczarzaki and S. rosetta CBP-KIX were generated using protein sequences E9CAO3 and F2TVQ2 respectively. Protein sequences were retrieved from UniProt. Human CBP-KIX (gray) was generated using PDB id 2LXT. In all the structures, MoRFs are highlighted in red color, C and N represented C-terminus and N-terminus, respectively.
