Figure 7.
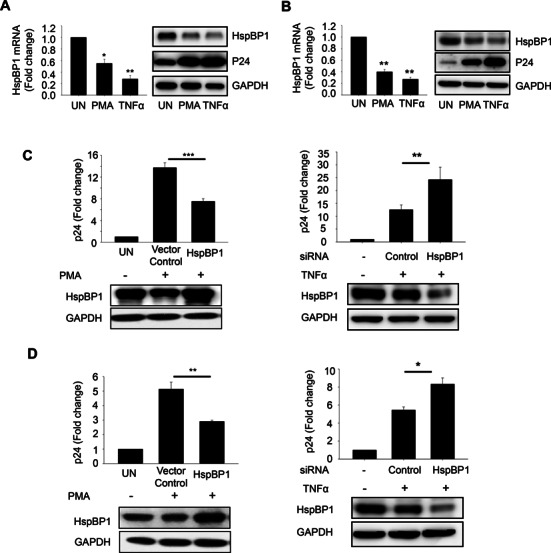
HspBP1 inhibits activation of latently infected cells. Activation of latently infected cells [(A) ACH2 and (B) U1] leads to depletion in HspBP1 levels. ACH2 and U1 were stimulated with PMA (50ng/ml) and TNFα (10 ng/ml). 36 h post-treatment, cells were harvested for RNA and protein lysate preparation. Expression of HspBP1 was analyzed by qRT-PCR and immunoblotting. (C) HspBP1 over-expression inhibits virus production whereas knockdown causes an increase in virus production in ACH2 cells. Nucleofection was performed to over-express or knockdown HspBP1 in these cell lines. 24 h post-nucleofection, cells were stimulated with PMA (50 ng/ml) or TNFα (10 ng/ml). 24 h post-activation, p24 ELISA was performed with the supernatant to determine the amount of virus produced. HspBP1 over-expression and knockdown was confirmed by immunoblotting. (D) HspBP1 over-expression inhibits virus production whereas knockdown causes an increase in virus production in U1 cells. The results shown in (A), (B) and (C) are representative of three experiments. (D) represents data from two experiments. Error bars represent the mean ± SD values and significance is defined as **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001.
