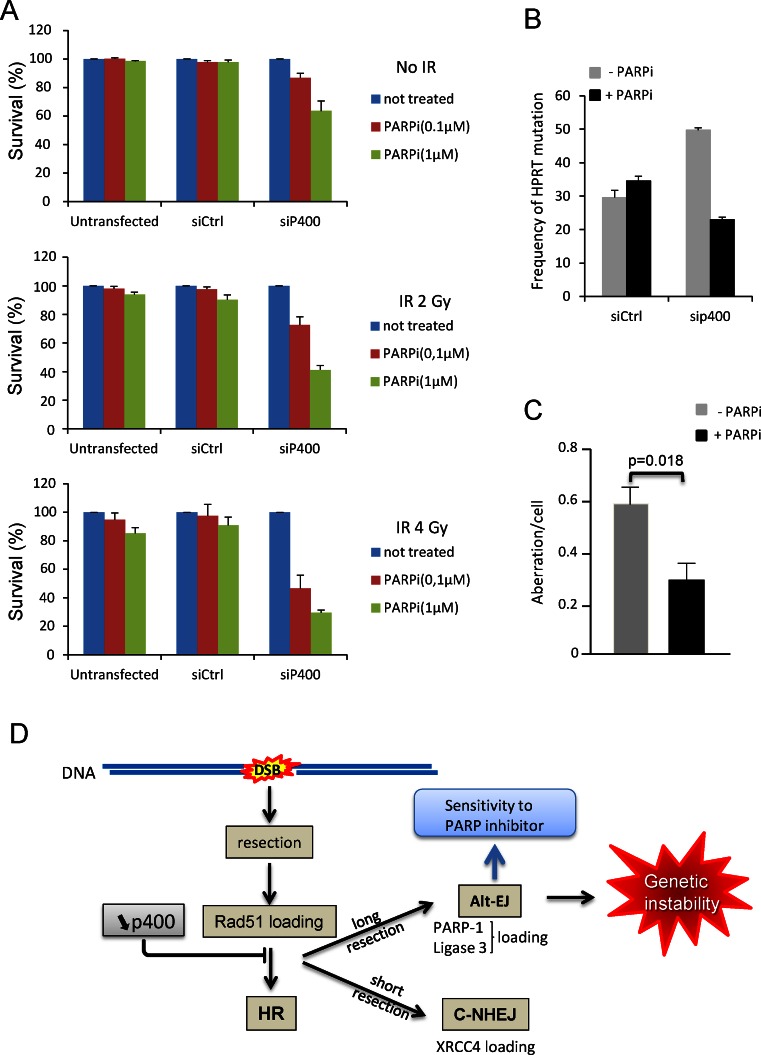
Figure 7.
p400 deficient cells are selectively sensitive to PARP inhibition. (A) Cells transfected with Ctrl or p400 siRNAs were treated with the PARP inhibitor olaparib and exposed or not to ionizing radiations and let grow for 10 days before colonies counting. The number of colonies in untreated cells (without olaparib) was set at 1. Results are from one representative experiment performed in triplicate on which mean and sd were calculated. The same experiment was repeated in totally independent experiment. (B) Effect of PARP inhibition on HPRT mutagenesis. Cells transfected with Ctrl or p400 siRNAs were treated or not with olaparib (1 μM) and exposed to ionizing radiations then selected for HPRT mutants by 6-thioguanine treatment. Results are expressed as frequency of HPRT mutation per million living cells. Results are from one representative experiment performed in triplicate. The same experiment was repeated in totally independent experiment. (C) Effect of PARP inhibition on chromosomal aberrations. Cells transfected with p400 siRNAs were treated or not with olaparib (1 μM) and exposed to ionizing radiations (2 Gy). Metaphase spreads were prepared and aberrations scored. For sip400 transfected cells untreated and treated with PARP inhibitor (n = 52) and (n = 53) metaphases were examined, respectively. Results are presented as mean ± standard error. (D) schematic representation of the p400 role in controlling HR and Alt-EJ and its consequences on genetic instability.