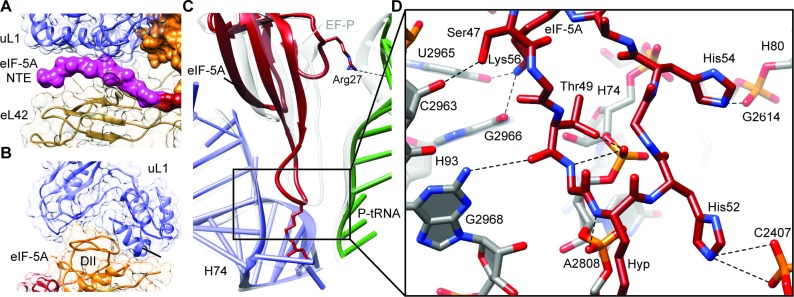
Figure 2.
Interaction of eIF-5A with the yeast 80S ribosome. (A) View of the NTE of eIF-5A sandwiched between ribosomal proteins uL1 (blue) and eL42 (tan). (B) Domain II (DII, orange) of eIF-5A inserts into the cleft between domains 1 and 2 of uL1 (blue). (C) Comparison of the ribosome binding position of domain I of eIF-5A (red), P-tRNA (green) and 25S rRNA helix 74 (H74, blue) relative to the EF-P, P-tRNA and H74 (gray) from the bacterial EF-P–70S complex (16). Arg27 of eIF-5A makes a potential hydrogen bond interaction (dashed line) with the P-tRNA (green). (D) Possible hydrogen bond interactions (dashed lines) between domain I of eIF-5A (red) with 25S rRNA nucleotides within helices H74, H80 and H93 of the ribosome (gray).