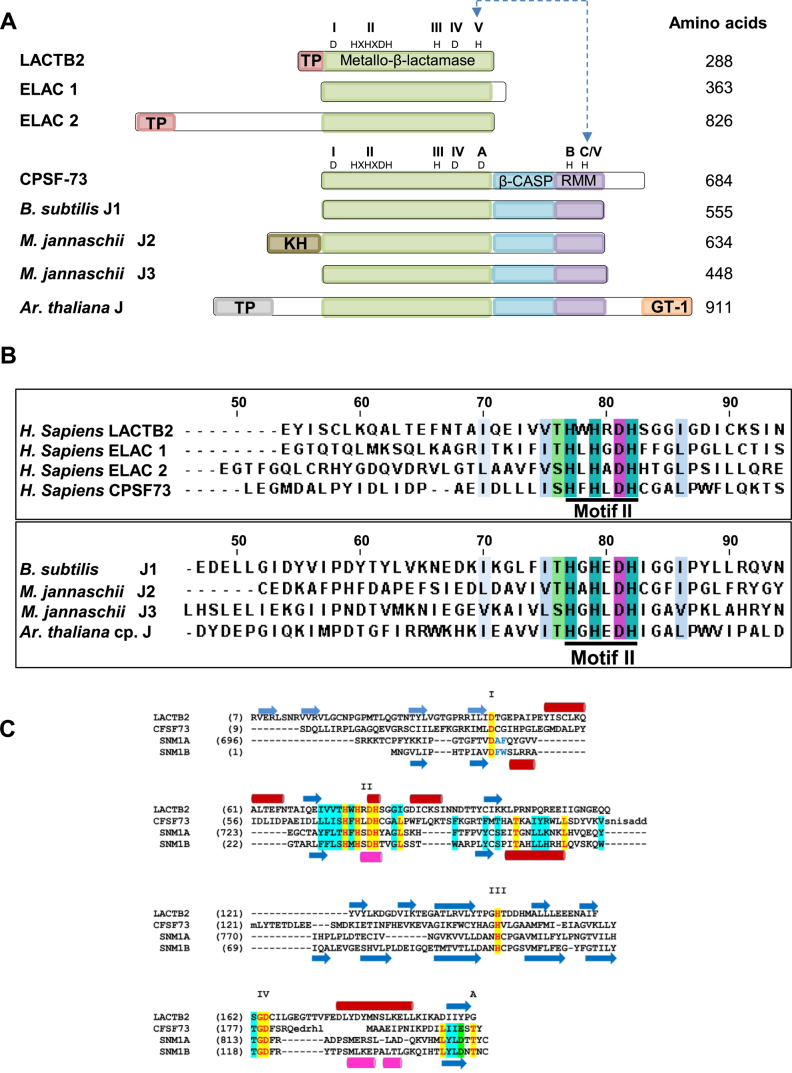
Figure 2.
LACTB2 is a member of the metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) superfamily. (A) Domain analysis comparison of LACTB2, ELAC1, ELAC2, CPSF-73 of human, as well as bacterial, archaeal and plant proteins that are members of β-CASP MBL subfamilies. The core domains of the following proteins were aligned: human metallo-β-lactamase protein like 2 (LACTB2) (Q53H82), human cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 73 (CPSF-73) (Q9UKF6), human nuclear tRNAseZ (ELAC1), human mitochondrial RNaseZ (ELAC2) (Q9BQ52), bacteria Bacillus Subtilis RNase J1 (B. subtilis J1) (Q45493), archaea Methanocaldoccous jannaschii RNase J2 and J3 (M. jannaschii J2 and M. jannaschii J3) (MJ1236, MJ0861), and plant Arabidopsis thaliana RNase J that is located in the chloroplast (A. Thaliana J) (Q84W56). The conserved motifs of the MBL, β-CASP and RRM (I–IV; A–C) are indicated in green, blue and purple, respectively, along with the diagnostic amino acid residues. The MBL and β-CASP proteins were mapped based on their structural alignment (29,32). Motif V of LACTB2, ELAC1 and ELAC2 shares a linear sequence alignment with Motif C of the β-CASP proteins, which is represented as C/V. Mitochondria and chloroplast transit peptides are colored in pink and gray, respectively. The archaeal N- terminal region corresponds to the KH RNA-binding domain (85) and the plant C-terminal region includes a putative GT1 DNA-binding domain (86). The number of amino acids of each protein is indicated to the right. (B) Alignment of the amino acid sequence of Motif II of LACTB2 and several MBL ribonucleases. CLUSTAL W and JalView were used for the alignment. The numbers above the amino acid sequence indicate the position of amino acids in human LACTB2. Signature MBL motif II, HXHXDH, is underlined with a thick black line and His (H) residues are highlighted in cyan and Asp (D) residues in purple. The intense cyan and purple colors represent the highest degree of conservation among the eight proteins while pale blue and green colors signify a lower degree of conservation. Uncolored residues represent no conservation within the annotated threshold. (C) Structure-based alignment of the MBL domains of LACTB2, CPSF73 and the DNA exonucleases SNM1A and SNM1B (all from humans). Secondary structural elements (blue arrows: β strands; red cylinders: α-helices) are shown above the alignment for LACT2B and below for CPSF73. The Roman numerals I–IV indicate the conserved MBL motifs, and the specific residues are indicated highlighted in yellow; less conserved sequences are highlighted in cyan. The alignment ends where the structures diverge (β-CASP region in CPSF73, SNM1A and SNM1B, and the unrelated C-terminal region of LACTB2).