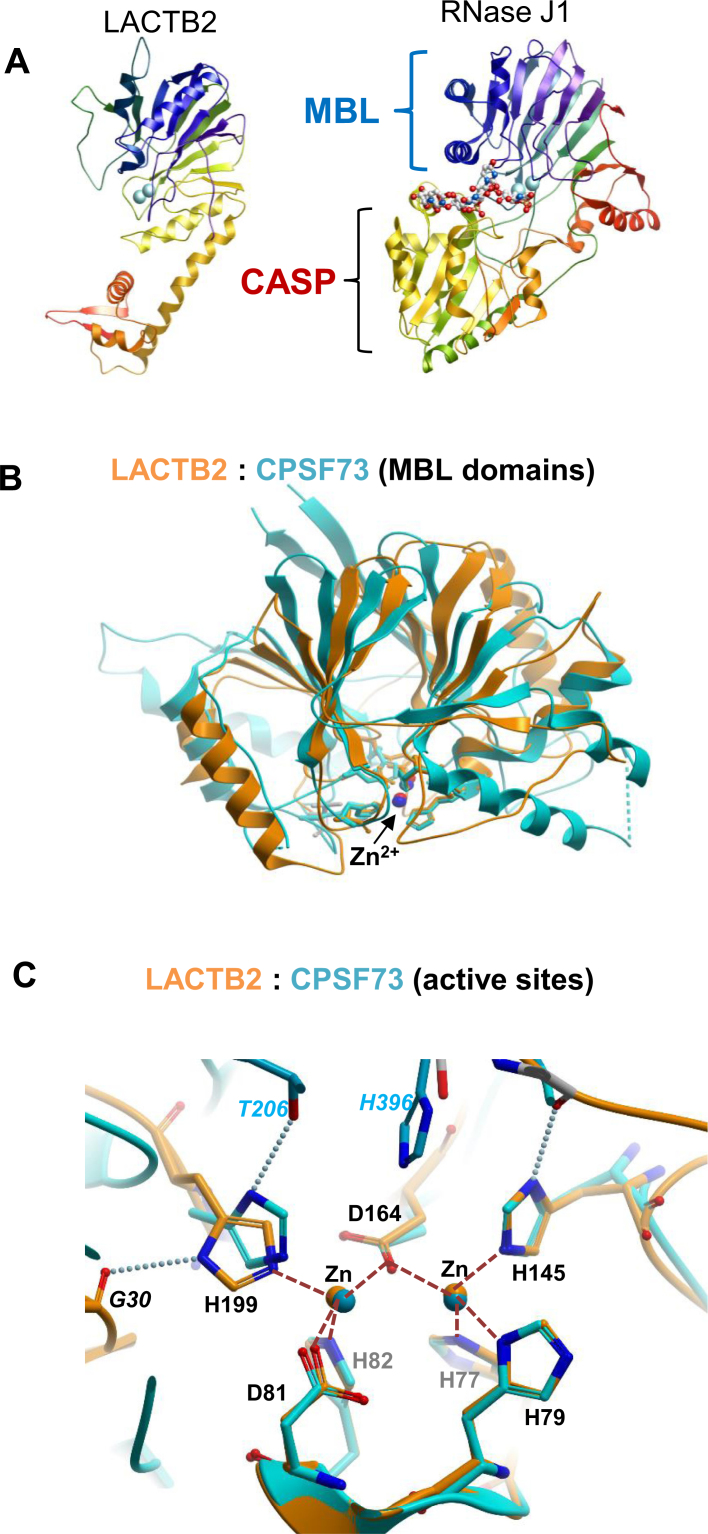
Figure 3.
Crystal structure of LACTB2 and comparisons with β-CASP ribonucleases. (A) Comparison of the overall fold of LACTB2 and RNase J1 (PDB ID: 3T3N). The chains are colored in blue to red from the N- to the C-terminal and the Zn ions are shown as cyan spheres. The RNase J structure also includes a bound RNA oligonucleotide, shown in stick representation. The common MBL fold is shown on the top in both proteins, while the CASP domain is present only on RNaseJ. The chain is colored as a rainbow spectrum from the N (blue) to C (red) terminus. (B) Superposition of the MBL domains of LACTB2 (aa 1–211 orange) and CPSF-73 (PDB ID: 2I7T, residues 9–207 and 395–459; cyan). (C) Closeup of the active sites of LACTB2 (orange) and CPSF-73 (cyan). The numbers of the homologous residues from LACTB2 (shown in the figure) and CPSF73 are, respectively, Motif II: His 77/71, His 79/73, Asp 81/75 and His 82/76. Motif III: His 145/158. Motif IV: Asp 164/179, and motif C/V: His 199/418. Motif I (Asp 46/39), which helps to orient His 82/76 but does not coordinate the zinc ions, is not shown. Motif A (Thr 230 in CPSF73), which helps to orient His 418, is conserved in SNM1A/B, but absent in LACTB2; His 199 of LACTB2 is instead supported by an interaction with the main-chain carbonyl of Gly 30. The Zn2+ ions are presented as spheres; coordination bonds as dashed orange lines, and selected hydrogen bonds are depicted as dotted lines. The His 396 residue belonging to motif B of the β-CASP domain of CPSF-73 that is lacking in LACTB2, is also indicated.