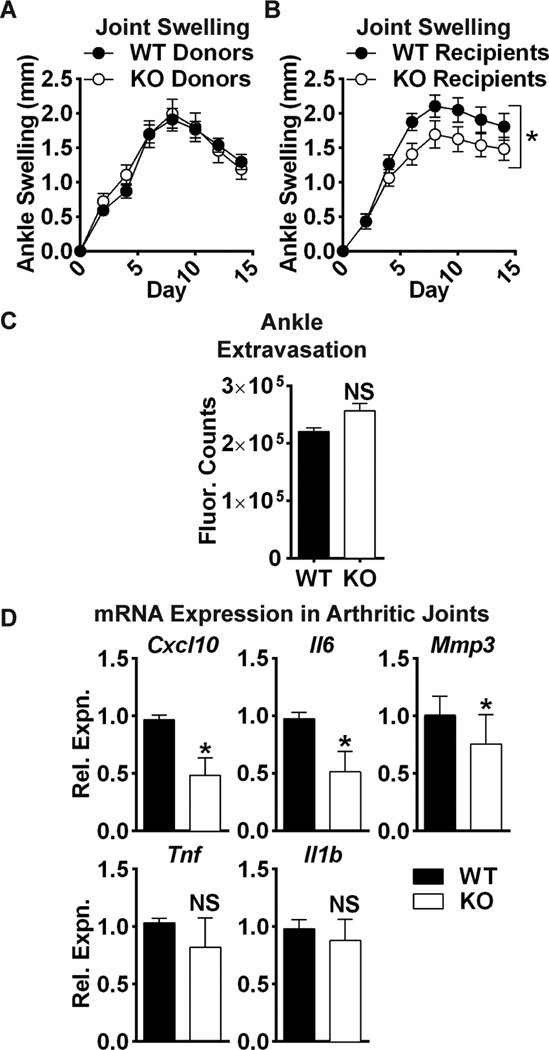
Fig. 6. Arthritis protection in Ptpra KO mice is dependent upon radioresistant cells.
(A–B) Mice were lethally irradiated and administered bone-marrow from donor mice. 10–11 weeks post-irradiation, arthritis was induced in recipients by administration of K/BxN sera. (A) Male WT congenic CD45.1 mice were administered bone-marrow cells from WT or Ptpra KO CD45.2 donor mice (WT donors, n=19; KO donors, n=18). (B) Male WT (n=11) or Ptpra KO (n=11) mice were administered bone-marrow cells from WT congenic CD45.1 mice. Mean ± SEM is shown. *, p<0.05, 2way ANOVA. (C) WT (n=5) and Ptpra KO (n=3) littermate mice were administered Angiosense 680 dye, followed by administration of K/BxN serum. Ankle fluorescence was monitored after 60 min. Median and IQR is shown. NS, non-significant, Mann-Whitney test. (D) WT (n=7) or Ptpra KO (n=7) mice were administered K/BxN sera. 8 days post-sera transfer, ankle joints were homogenized and mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR. Median and IQR is shown. *, p<0.05, NS, non-significant, Mann-Whitney test.