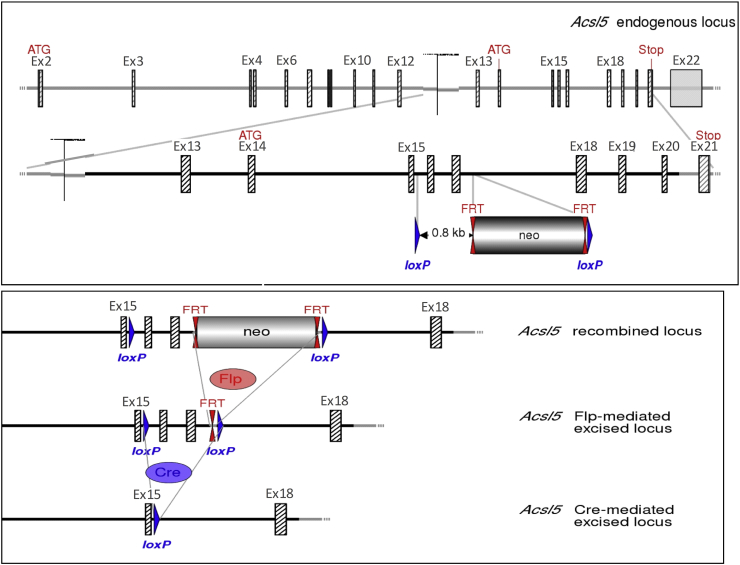
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of Acsl5 targeting strategy, resulting in deletion of exons 16–17. Diagram is not depicted to scale. Hatched rectangles represent Acsl5 coding sequences, gray rectangles indicate non-coding exon portions, and solid lines represent chromosome sequences. In upper panel, the initiation (ATG) and Stop (Stop) codons are indicated. FRT sites are represented by double red triangles and loxP sites by blue triangles. The size of the flanked Acsl5 sequence to be deleted is shown. The strategy results in the deletion of 206 bp of coding sequences encoding for part of the AMP binding domain. The splicing of exon 15 to exon 18 will lead to a frame shift resulting in a premature stop codon in exon 20. In lower panel, the scheme of Cre recombinase- or Flp recombinase-mediated excision at the recombined Acsl5 locus.