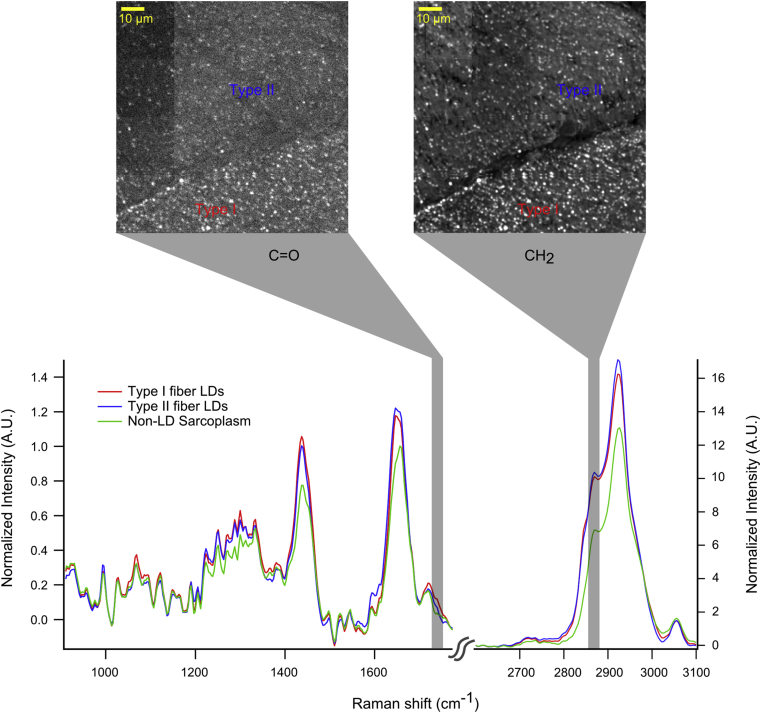
Figure 6.
Quantitative imaging of lipid droplet chemistry in muscle using hyperspectral CARS microscopy. One complete hyperspectral dataset contained spectral data from Type I and Type II muscle fibers in a human muscle biopsy of m. vastus lateralis. LDs were identified from the tissue based on image thresholding similar to [39] and additional data segmentation was performed to group LDs by fiber type. This allowed for producing LD specific spectra from each fiber type and from the non-LD area. Average spectra from LDs in Type I (red) and Type II (blue) fibers and the total non-LD area (green) highlight differences in chemical environment between the LDs between different fiber types and from LDs to the sarcoplasm. Images show chemical images of esters (C O) and CH2 symmetric vibrations. LDs in type I fibers contain more esters, yet similar CH2, compared with Type II fibers, which suggests a differential type of neutral lipid storage between fiber types in the same muscle. (Unpublished data, SD, MKCH, and SHP).