Figure 3.
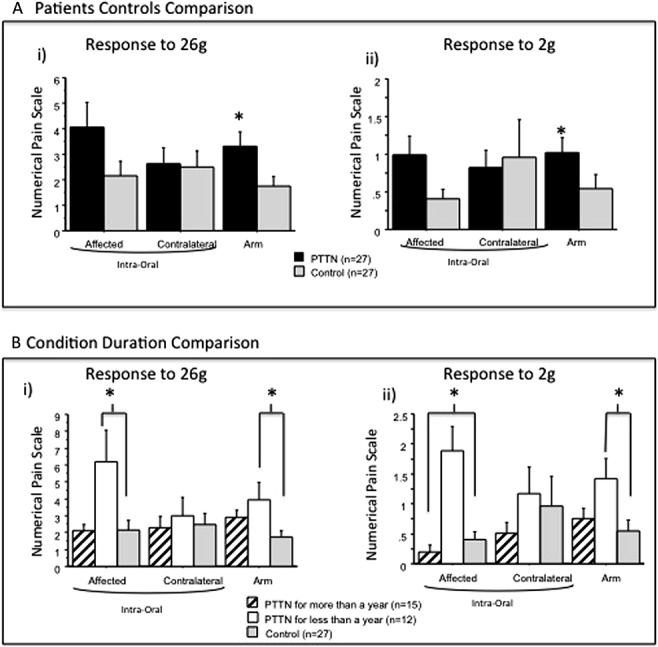
Responses to 2g and 26g stimulation on a 0 to 20 numerical pain scale were recorded from painful posttraumatic trigeminal neuropathy (PTTN) patients and healthy control subjects. Results show evaluations in the subjects' affected (injured) and contralateral intraoral sites and on the dominant forearm. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Nonparametric analysis was used to compare the difference between study groups. The exact Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to compare the medians of 2 groups (PTTN and control), and the exact Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare the medians across multiple groups (PTTN > 1 year, PTTN < 1 year, and controls). (A) The arm response rating to 26g and 2g stimuli was significantly (*) elevated in the PTTN group compared with the control group. In the affected and contralateral sides, no significant differences were found between the PTTN and control groups. (B) Patients with PTTN for less than a year had a significantly (*) elevated response to 26g and 2g stimuli in the affected side compared with patients with PTTN who suffer from the condition for more than a year and controls. In the arm, patients with PTTN for less than a year had a significantly (*) elevated response to 26g and 2g stimuli compared with controls but not compared with patients with PTTN who suffer from the condition for more than a year.
