Fig. 1.
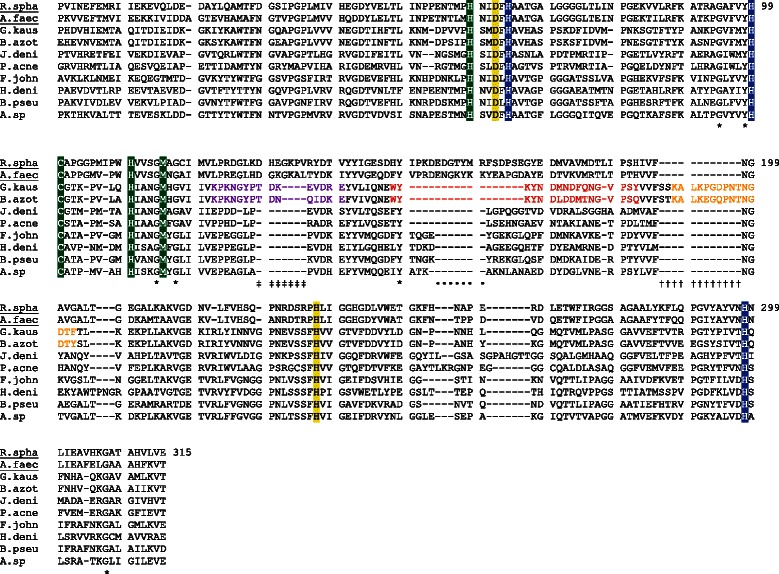
Trimmed multiple sequence alignment of NirK from Rhodobacter sphaeroides ATCC 17025 (R. spha), Alcaligenes faecalis S-6 (A.faec), Geobacillus. kaustophilus HTA426 (G.kaus), Bacillus azotoformans LMG 9581 T (B.azot), Jonesia denitrificans DSM 20603 (J.deni), Propionibacter acnes C1 (P.acne), Flavobacteria johnsoniae UW101 (F.john), Halomonas denitrificans ATCC 35960 (H.deni), Burkholderia pseudomallei 668 (B.pseu) and Azospirillum sp. B506 (A.sp). Sequences belonging to Clade I NirK are underlined. Amino acid numbering was based on the full-length NirK sequence of Rhodobacter sphaeroides ATCC 17025. The linker, tower and extra loop specific for Bacillus sp. are given in purple, red and orange respectively. Copper binding motives T1Cu and T2Cu are indicated in green and blue respectively, active site residues Asp and His required for nitrite reducing activity in yellow, conserved regions are indicated by *, deletions specific to Clade II NirK sequences are indicated by ‡ and • and the Bacillus specific insertion by †
