Figure 2. β-catenin silencing down-regulates PTMA protein level and potentiates sorafenib-induced cell death in HCC cells.
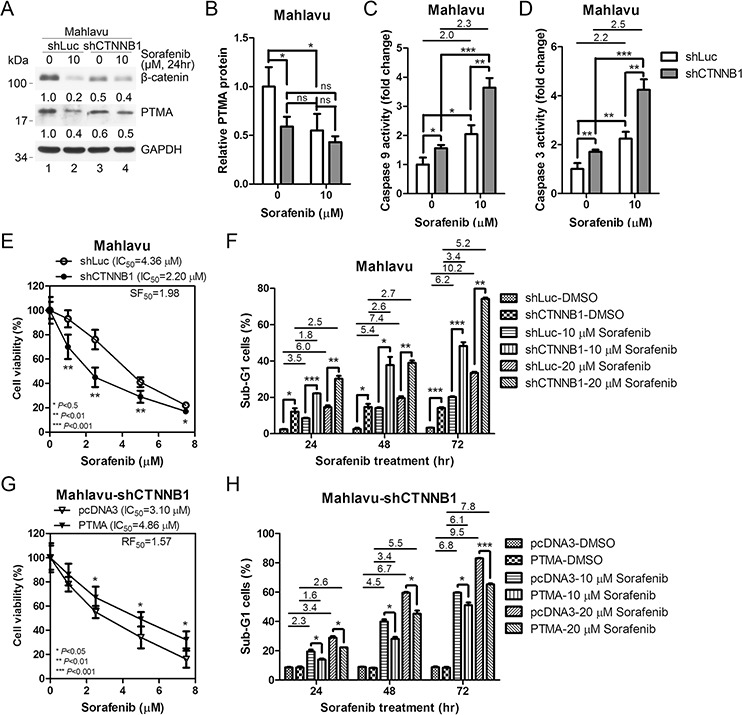
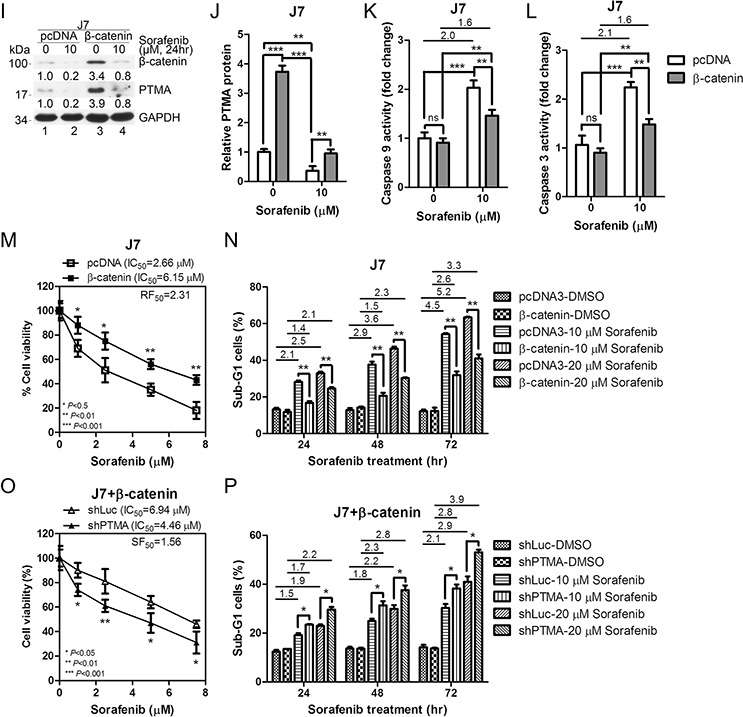
A. Down-regulation of PTMA protein level by β-catenin silencing (shCTNNB1) and sorafenib. Silencing caused inhibition of β-catenin by 50%. Fold change, relative to the control (first lane), is indicated. B. Quantification of PTMA protein level of (A) The relative protein level indicated (each lane was first normalized to GADPH) was calculated against the shLuc control. Increased activation of caspase-9 C. and caspase-3 D. by sorafenib following β-catenin silencing in Mahlavu cells. E. Sensitization of Mahlavu cells to sorafenib following β-catenin silencing. Cell sensitivity was assessed using the MTT assay. IC50 and sensitization factor (SF50) are indicated. SF50 was calculated by dividing the IC50 of control shLuc cells by that of shCTNNB1 cells. F. Enhancement of sorafenibinduced sub-G1 cells following β-catenin silencing. G. Ectopic expression of PTMA rescues sorafenib sensitivity in shCTNNB1-expressing Mahlavu cells. H. Reduction of sorafenib-induced sub-G1 cells following PTMA overexpression in shCTNNB1-expressing Mahlavu cells. I. Enhancement of PTMA following overexpression of β-catenin in J7 cells. J. Quantification of PTMA protein level of (I) Increased activation of caspase-9 K. and caspase-3 L. by sorafenib following β-catenin silencing in Mahlavu cells. M. Ectopic expression of β-catenin protects J7 cells against sorafenib. N. Reduction of sorafenib-induced sub-G1 cells following β-catenin overexpression. O. Sensitization of β-catenin-expressing J7 cells to sorafenib following PTMA silencing. P. Enhancement of sorafenib-induced sub-G1 cells in β-catenin-overexpressing J7 cells by PTMA silencing. Fold change between treatments is also indicated. Results of three experiments are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
