Figure 2. Schematic of the diverse effects of M1 and M2 macrophages on bladder cancer cells.
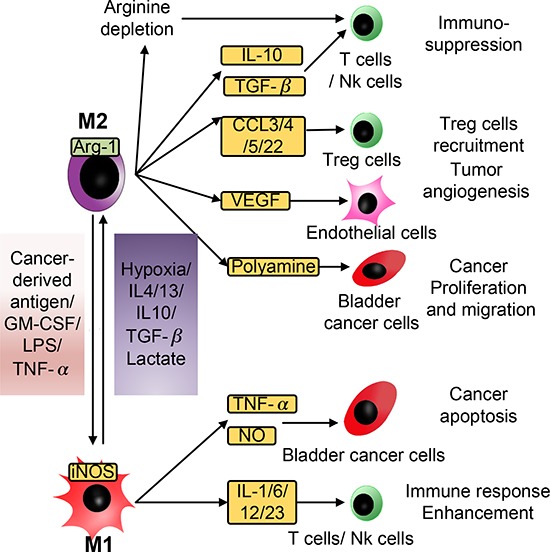
Macrophages are highly versatile immune cells that can exert anti- and pro-tumor effects at the same time. The M1/M2 model is usually used to interpret the complicated nature of macrophages. In response to stimulation by cancer-derived antigens, LPS, or TNF-α, TAMs become M1 macrophages, secrete NO and TNF-α to facilitate the apoptosis of cancer cells, and secrete IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, and IL-23 to enhance the immune response. When stimulated by hypoxia, IL-4, IL-13, IL-10, TGF-β, or lactate, TAMs polarize into M2 macrophages and cause immunosuppression, tumor angiogenesis, proliferation and migration by secreting a series of immune-regulating factors including IL-10, TGF-β, CCLs, VEGF, and polyamine.
