Figure 7. Schematic of the effect of lactate shuttling on the reprogramming and recruitment of macrophages.
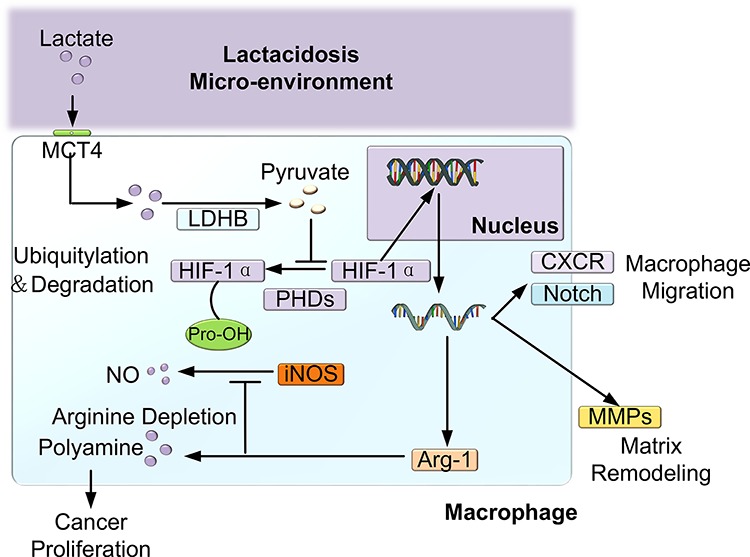
Lactate was secreted into the tumor microenvironment via MCT4 and was then transported into macrophages via MCT1. Subsequently, lactate was metabolized to pyruvate by LDH1; then, pyruvate competitively inhibited the activity of PHDs, which prevented the ubiquitylation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and its destruction by the proteasome. Subsequently, HIF-1α may create “pseudo-hypoxia” by enhancing the transcription of a series of hypoxia-related genes, such as Arg-1, which metabolizes arginine to provide substrates for cancer cell proliferation. Additionally, HIF-1α may activate the transcription of the C-X-C chemokine receptor (CXCR) and Notch [25, 26], which are important signaling factors in cell migration. Furthermore, HIF-1α can promote matrix remodeling by increasing the secretion of MMPs.
