Figure 1.
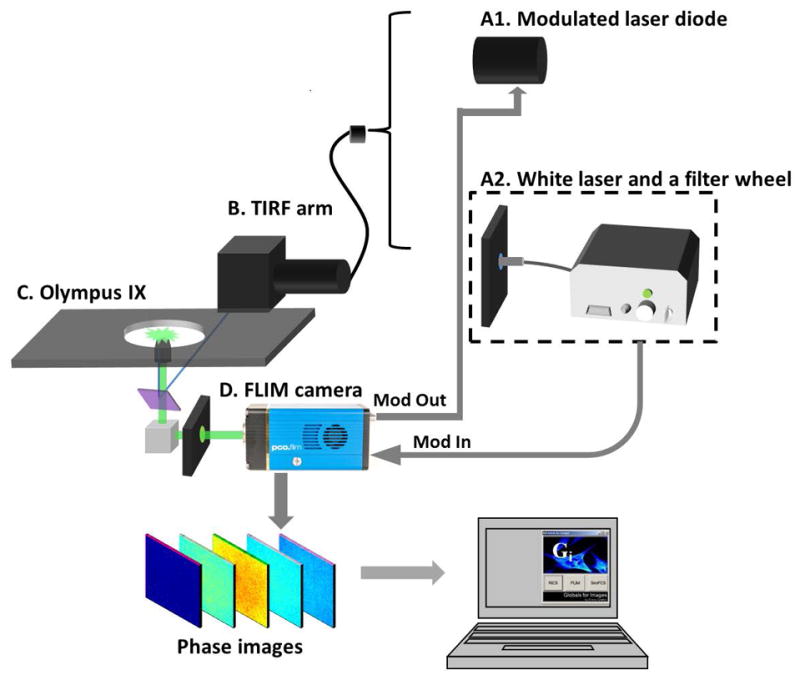
Schematic of the CMOS based widefield FD-FLIM system. A1) A 440 nm laser diode (ISS Inc, USA) which can be modulated by the FLIM camera. A2) A 10 ps, 20 MHz supercontinuum laser (SC390, Fianium Inc, USA). Bandpass filters were used to select proper excitation wavelengths. A heat blocker (KG-5, Edmund Optics, USA) was added into the excitation path to reduce the heat. B) The excitation beam was coupled into a commercial Olympus TIRF microscope (Olympus, USA) via the TIRF arm. C) Experiments were done with a 60× (NA=1.45) oil-immersion TIRF objective (Olympus, USA). The fluorescence signal was collected by the same objective. D) The bottom prism of the Olympus microscope reflected this signal to the pco.flim CMOS camera (PCO AG, Germany). The FLIM camera was controlled by a computer for modulation and data acquisition. Acquired phase images are analyzed by SimFCS software.
