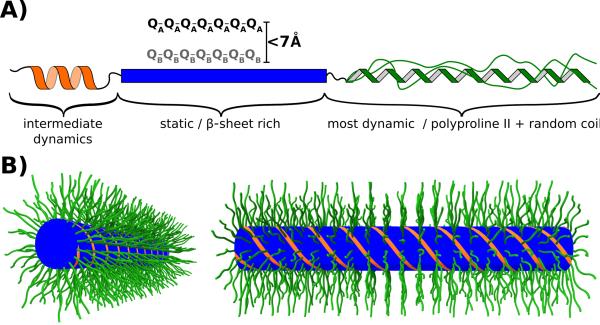
Figure 7.
(A) Model illustrating the dynamic and structural heterogeneity of the httex1 monomers found in 4°C fibrils. The N17 fragment, which was shown to be in an α-helical conformation, was difficult to detect in our spectra probably due to intermediate dynamics. The polyQ domain is static and features two types of Gln, A and B, which are separate in sequence but relatively close in space. The C-terminus has Pro residues in a polyproline II conformation and Pro and other non-Pro residues in a random coil conformation. The C-terminus is the most dynamic domain in httex1 fibrils albeit with considerable dynamic heterogeneity due to relatively static Pro residues as detected in our spectra. (B) Bottlebrush model of httex1 4°C fibrils. The N17 (orange) and polyQ (blue) domains form the center of the fibril. The Proline-rich C-termini (green) are flexible, partially disordered and pointing away from the center forming the bristles in this bottlebrush model.